FAQs
About Psychology
The College of Psychologists of Ontario regulates the profession of psychology in Ontario. Members of the College are regulated professionals and are the only persons authorized to practice psychology in the province. Psychologists and Psychological Associates are members of the College.
The College is not a university, community college, or school. Instead, its mandate is to protect the interests of the public by ensuring that consumers receive competent and ethical professional psychological services from qualified providers.
Regulated professionals are required by law to deliver professional services competently and ethically. They are accountable to the public, through their professional regulatory body, for their professional behaviour and activities. As members of the College of Psychologists of Ontario, Psychologists and Psychological Associates must meet rigorous professional entry requirements, adhere to prescribed standards, guidelines, and ethical principles and participate in quality assurance activities to continually update and improve their knowledge and skill.
In contrast, the College has no authority over unregulated service providers. There is no regulatory body with the legal authority to set minimum levels of education, training, and competence or to establish and monitor professional and ethical standards of conduct. There is no professional regulatory body responsible to protect your interests and hold unregulated providers accountable for the services you receive.
Only members of the College of Psychologists of Ontario may use the title ‘Psychologist’ or ‘Psychological Associate’; use the terms ‘psychology’ or ‘psychological’ in any description of services offered or provided, or hold themselves out to be a Psychologist or Psychological Associate. Psychologists and psychological associates respectively may also identify themselves with the designation C.Psych. or C.Psych.Assoc. after their names.
To qualify for professional registration to practise psychology requires successful completion of graduate education and training in professional psychology, supervised professional experience, and examinations. A member of the College is required to practise in accordance with applicable legislation, regulations, standards of conduct, professional guidelines, and professional codes of ethics.
Psychologists and Psychological Associates are trained in the assessment, treatment, and prevention of behavioural and mental conditions. They diagnose neuropsychological disorders and dysfunctions as well as psychotic, neurotic and personality disorders and dysfunctions. In addition, Psychologists and Psychological Associates use a variety of approaches directed toward the maintenance and enhancement of physical, intellectual, emotional, social and interpersonal functioning.
Psychologists and Psychological Associates usually focus their practice in specific areas such as clinical psychology, counselling psychology, clinical neuropsychology; school psychology; correctional/forensic psychology; health psychology; rehabilitation psychology; or industrial/organizational psychology. Within these areas, a Psychologist or Psychological Associate may work with a variety of individual client populations such as children, adolescents, adults or seniors, or may focus their attention on families, couples, or organizations. They work in a range of settings including schools, hospitals, industry, social service agencies, rehabilitation facilities, and correctional facilities. Many Psychologists and Psychological Associates have their own private practice.
A Psychologist or Psychological Associate who holds a certificate of registration authorizing autonomous practice may provide services without supervision, within his or her area of competence, and may charge a fee for these services. While most members of the College have no explicit term, condition, or limitation on their certificates of registration, some do and must practice in accordance with any such restriction.
The College maintains a register of all current members. Information about an individual Psychologist or Psychological Associate may be found in the searchable Public Register or obtained from the College by telephone 416-961-8817or by e-mail: cpo@cpo.on.ca.
Occasionally clients of Psychologists and Psychological Associates need to have forms completed and signed by their treating professional in order to obtain insurance reimbursement for psychological services or to qualify for some other benefit or service from an insurer or government agency. Normally both Psychologists and Psychological Associates may complete and sign such forms. If there are any questions or difficulties in having such forms accepted, please contact the College for guidance.
The difference is in how they are trained. Both have completed an undergraduate degree and have gone on to complete a graduate degree in psychology.
Psychological Associates have completed a masters level degree in psychology (e.g. M.A., M.Sc., M.Ps., M.Ed.), which is then followed by four years of experience working in the scope of practice of psychology. Psychologists have completed a doctoral level degree in psychology (Ph.D., Psy.D., Ed.D., D.Psy.) which typically includes a one-year internship.
Both Psychologists and Psychological Associates have then completed at least one additional year of formal supervised experience approved by the College and passed the three examinations required by the College.
The profession of psychology in Ontario has a single scope of practice. There is no distinction made in the legislation or in the regulations between Psychologists and Psychological Associates with respect to scope of practice or with respect to controlled/authorized acts.
All members must have knowledge and skills respecting interpersonal relationships, assessment and evaluation, intervention and consultation, understanding and applying research to professional practice and knowing and applying professional ethics, standards and relevant legislation to professional practice. Every member of the College, with the exception of individuals whose practice is limited to Industrial/Organizational Psychology, must be competent to formulate and communicate a psychological diagnosis.
*Note: In June 2009, the Federal/Provincial Agreement on Internal Trade was signed and in December 2009, the Ontario Labour Mobility Act (2009) was enacted. As a result of this legislation, the College must offer registration as a Psychologist to individuals who have been registered as Psychologists in other Canadian jurisdictions, regardless of the level of their graduate degree in psychology. There are some Canadian jurisdictions that award the title Psychologist to individuals at the Masters, rather than Doctoral level. The recent legislation requires that the College recognize this title for these individuals. Therefore, while the majority of psychologists and psychological associates in Ontario will have the differential training and experience described above, there are some Psychologists, who have come to Ontario from another Canadian jurisdiction, who may have a Masters degree. Members of the College are required to indicate their degree and title in any professional correspondence, report or promotional information.
In summary, both Psychologists and Psychological Associates are members of the College and are qualified psychological practitioners in the province of Ontario.
Questions?
Questions regarding Psychologists and Psychological Associates or other inquiries related to the regulation and practice of psychology in Ontario may be directed to the College:
The College of Psychologists of Ontario
Suite 500 – 110 Eglinton Avenue West
Toronto, Ontario M4R 1A3
Tel: (416) 961-8817/(800) 489-8388
Fax: (416) 961-2635
E-mail: cpo@cpo.on.ca
Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA)
Yes, the Peer Assessment may be conducted in-person or virtually. Any confidential documentation must be shared via a secure platform, and either anonymized or with the consent of the client.
Behaviour Analyst Transitional Route 2 applicants can download the Attestation A/B, Attestation C, and Peer Assessment Forms from the “Download Documents” section in the application portal or from the “Become a Member” section of the Reference Library.
Behaviour Analyst applicants must have the relevant organization submit the following supporting documents directly to the College: transcript(s), BACB® verification letter, and letters of good standing from other regulatory Colleges/Boards (if applicable).
E-mail is preferred: cpo@cpo.on.ca. If e-mail is not possible, please have the organization mail the document to:
The College of Psychologists of Ontario
110 Eglinton Ave West, Suite 500
Toronto, ON
M4R 1A3
Regarding the Vulnerable Sector Check, applicants may e-mail or upload it to their application form. Please contact the College if your region does not issue Vulnerable Sector Checks for registration purposes.
Yes, the incoming Psychology and Applied Behaviour Analysis Act (2021) requires Transitional Route 1 applicants to hold active BCBA® or BCBA-D® certification at the time that their certificate of registration authorizing autonomous practice as a Behaviour Analyst is issued by the College (i.e. from July 1, 2024 onwards). After an applicant receives their certificate from the College, they may decide to maintain their BCBA® or BCBA-D® certification or not. Registration will be the minimum requirement for practicing as a Behaviour Analyst, BACB® certification will be above and beyond registration.
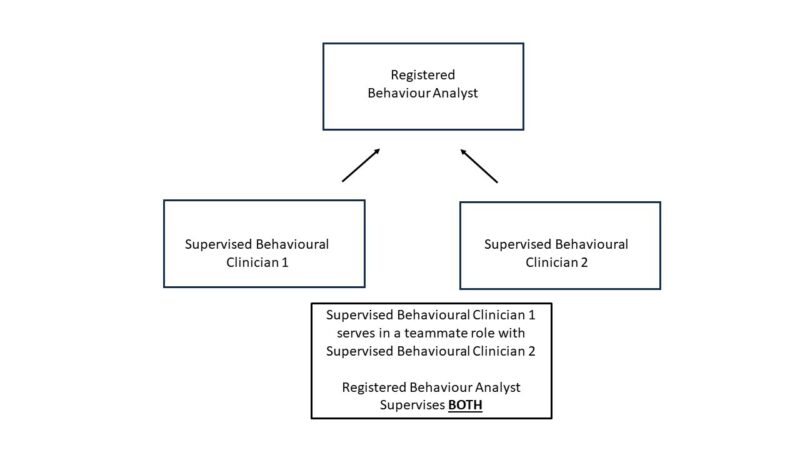
Supervision is defined as:
…an ongoing educational, evaluative and hierarchical relationship, where the supervisee is required to comply with the direction of the supervisor, and the supervisor is responsible for the actions of the supervisee.
Supervision in ABA is a regulated professional service. The ABA supervisor is in a hierarchical relationship with their supervisees, whereby the supervisees must comply with the supervisor’s direction.
Models of care in ABA can sometimes include multiple teammates working together to serve a client’s needs.
The College does not permit “second-order” supervision. This means that, while a Behaviour Analyst’s supervisees may have varying roles and responsibilities as among themselves, including some oversight or supervisory roles, the Behaviour Analyst is directly responsible for all supervisees.
It may be helpful to think of the Behaviour Analyst as the one responsible for all services provided to the client. There may be multiple individuals involved in providing those services, who may have varying roles and responsibilities. The Behaviour Analyst is responsible for all the individuals involved in the provision of services to clients. The illustration above is meant to assist in emphasizing the Behaviour Analyst’s supervisory responsibilities across different models of care.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is the application of the science of learning to understand and improve behavior that is meaningful to the person and those around them. ABA considers how the environment impacts learning. The term behaviour refers to anything a person says or does, including skills and actions needed to talk, play, and live. Behavior can also be private (e.g., thoughts and feelings).
ABA can help increase helpful or functional skills (e.g., communication) and/or decrease behaviours that are harmful or interfere with learning (e.g., self-injury).
ABA intervention uses evidence-based procedures such as positive reinforcement to address a client’s concerns and needs and to reduce interfering behaviour and increase desirable behaviour. Behaviour Analysts practice in a variety of settings with many different client populations.
Resources:
- The Ontario Association for Behaviour Analysis (ONTABA) has developed this graphic to describe ABA, what it is and what it is not. The graphic and more information can be found on their website.
- The Behavior Analysis Certification Board (BACB) has additional information on its website about the profession of ABA and the client populations it serves.
In 2017, the Minister of Health and Long-Term Care asked the Health Professions Regulatory Advisory Council (HPRAC) to provide advice on:
- What activities or aspects associated with ABA therapy pose a significant and inherent risk of harm (if any), and whether the risk of harm of this therapy varies by client population (e.g., children and adults); and
- If there is a risk of harm, what is the range of options for an approach to oversight that could be considered?
In HPRAC’s January 2018 report to the Minister of Health and Long-Term Care, Applied Behaviour Analysis: Risk of Harm and Oversight, it concluded:
“Based on the evidence reviewed, HPRAC affirms that there is a risk of harm associated with most ABA interventions for clients, therefore oversight is recommended. Several oversight options to regulating providers were examined with a particular focus on clinical supervisors.”
With respect to oversight, HPRAC recommended the following:
“Because ABA therapy is deemed to pose a significant and inherent risk of harm across many client populations, HPRAC recommends that ABA providers performing a clinical supervisory role be regulated under an established health regulatory college, governed by the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 (RHPA). Other ABA providers would be accountable to the regulated clinical supervisors.”
To protect the public from risk of harm, once regulated Behaviour Analysts who supervise and/or deliver ABA interventions will have to meet clearly defined standards. These standards will include having the necessary knowledge, skills, and judgement to meet practice requirements and to be allowed to use the regulated title “Behaviour Analyst”.
Anyone who wants to practise a regulated health profession in Ontario, i.e., psychologists, psychological associates, physicians, nurses, dentists, occupational therapists etc., and now, Behaviour Analysts, must be registered with, and be accountable to, a health regulatory College. A College is not a university, community college, or school. Instead, its mandate is to protect the interests of the public by ensuring that clients receive competent and ethical professional services from qualified providers.
Ontario Health Regulators includes the 26 health regulatory Colleges in Ontario, including the College of Psychologists of Ontario. To learn more about how and why health professions are regulated in Ontario, visit their website.
Regulated professionals are required, by law, to deliver professional services competently and ethically. They are accountable to the public, through their regulatory body, for their professional behaviour and activities. Once regulated, Behaviour Analysts will have to meet rigorous professional entry requirements, adhere to prescribed standards, guidelines and ethical principles and participate in quality assurance activities to continually update and improve their knowledge and skill. Complaints and discipline processes hold professionals accountable when a client, or other member of the public, believes that the standards may have been breached.
In contrast, the College has no authority over unregulated service providers. There is no regulatory body with the authority to set minimum levels of education, training, and competence or to establish and monitor professional and ethical standards of conduct. There is no professional regulatory body responsible to protect your interests and hold unregulated providers accountable for the services you receive.
On June 3, 2021, the enabling legislation to authorize the College of Psychologists of Ontario to regulate the profession of Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA), Bill 283, Advancing Oversight and Planning in Ontario’s Health System Act, 2021 received Royal Assent. Included in Schedule 4 of this Bill is the legislative authority for the College to regulate the profession of Applied Behaviour Analysis. On July 1, 2024 this legislation will be proclaimed by the government and will repeal the Psychology Act, 1991 to replace it with the Psychology and Applied Behaviour Analysis Act, 2021.
The new Act establishes the regulation of two separate and distinct professions, Psychology and Applied Behaviour Analysis within one College. The current College of Psychologists of Ontario will be the regulator for both professions and will be renamed the College of Psychologists and Behaviour Analysts of Ontario to reflect its expanded role. The legislation maintains the regulatory framework for current members, Psychologists and Psychological Associates, but additionally:
- Defines the scope of practice for ABA: “The practice of applied behaviour analysis is the assessment of covert and overt behaviour and its functions through direct observation and measurement, and the design, implementation, delivery and evaluation of interventions derived from the principles of behaviour in order to produce meaningful improvements”;
- Restricts the use of the title “Behaviour Analyst” to members of the new College registered as Behaviour Analysts;
- Expands the “Representations of Qualifications” restriction to include holding oneself out as qualified to practice as a Behaviour Analyst or in a specialty of behaviour analysis; and
- Updates the size and composition of the current College’s Council to enable fair representation for both professions.
In 2017, the Health Professions Regulatory Advisory Council (HPRAC), at the request of the then Minister of Health and Long-Term Care, undertook to review Applied Behavioural Analysis; its potential for harm and need for regulation. In response to a request for information, the College submitted a letter which stated, in part, that, “Should ABA regulation proceed in Ontario, the Council of the College of Psychologists is prepared to undertake this process within its governance structure”.
On September 19, 2019, the College received a letter from Minister Todd Smith of the Ministry of Children, Community and Social Services and Minister Christine Elliott of the Ministry of Health inviting the College to confirm its interest in undertaking the regulation of ABA as part of its governance structure. In their letter, the Ministers state that, “Strengthening the oversight of behavioural clinicians will protect vulnerable Ontarians from risk of harm and set standard expectations for professional standards and educational requirements for ABA providers across the province. It will also support families in finding qualified providers, and making complaints about providers, if necessary. Our ministries would like to begin with regulating those who are in a supervisory role, and we envision that this will be broadened to include front-line clinicians over time.”
On September 27, 2019, the Council of the College of Psychologists passed a motion confirming the offer to undertake the regulation of ABA within its governance structure.
On July 20, 2023, the Ontario Government approved the regulations made under the Psychology and Applied Behaviour Analysis Act, 2021, for the profession of Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA). The Act will be proclaimed effective July 1, 2024, when the College will change its name to the “College of Psychologists and Behaviour Analysts of Ontario”. Beginning on that date, only ABA practitioners who are registered with the College of Psychologists and Behaviour Analysts of Ontario will be allowed to use the title “Behaviour Analyst” in Ontario.
The College is actively working on the by-law and policy changes that will be necessary to support the regulation of Behaviour Analysts. This work must be completed before the Act can be fully proclaimed by the government. The new Act and any other legislative changes will come into force on July 1, 2024.
Any person wishing to use the title “Behaviour Analyst”, a variation or abbreviation or an equivalent in another language, must register with the College. This would apply to clinical supervisors who provide clinical direction and supervision of ABA activities, which include behaviour assessment, designing an intervention plan, implementing intervention plans, and monitoring and evaluating the plans. Beginning on July 1, 2024, and going forward, only those who have registered with the College will have access to the restricted title “Behaviour Analyst”.
Service providers who deliver ABA interventions directly to a client or caregiver and are accountable to a Behaviour Analyst clinical supervisor will not be regulated.
Preregistration for Behaviour Analysts applying via Transitional Routes 1 and 2 opened on April 2, 2024. The goal of the pre-registration period is to ensure that qualified Behaviour Analysts can continue to practice and provide services to their clients on the date of proclamation and after, ensuring continuity of care. The College will not be accepting applications for supervised practice during the pre-registration period.
For more information, visit the Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA) Portal on the College of Psychologists of Ontario’s website, watch the College’s recently released video information session on the regulation of ABA, review the FAQs page for answers to frequently asked questions, or contact the College at aba@cpo.on.ca.
For most current members of the College, adding the profession of applied behaviour analysis to the College will have little or no effect. The College will regulate the two professions separately. Therefore, Psychologists and Psychological Associates should not see any change in their interactions with the College with respect to their practice or expectations of the College.
Behaviour Analysts will have their own standards of practice, quality assurance program and registration requirements. The current Professional Misconduct, Advertising and Quality Assurance Regulations will be revised so that they apply to the practice of applied behaviour analysis as well as psychology. The College Council will be enlarged and both Council and Committees will be made up of Psychologists, Psychological Associates, Behaviour Analysts, and public members appointed by the government. Decisions made by the College’s statutory committees will rely on the expertise of members of both professions and the public members who participate on each Committee.
There are members of the College who may also want to register as Behaviour Analysts in order to be able to use the restricted title “Behaviour Analyst”. They will hold two certificates of registration: one authorizing the practice of psychology and one authorizing the practice of applied behaviour analysis. These members will be expected to meet the College’s registration criteria and practice expectations with respect to both professions.
There is no connection between the regulation of Behaviour Analysts and the closure of master’s level registration for the practice of psychology. Any activity related to the closure of master’s level registration will be done separate and apart from activities undertaken to begin the regulation of Behaviour Analysts.
The scope of practice or activities that a Behaviour Analyst performs when providing services to a client are not Controlled Acts or restricted activities. They are therefore, in the public domain. If one is not registered with the College, one must be aware of the restrictions within the Act regarding how one refers to themselves in the course of providing services in applied behaviour analysis.
Once the Psychology and Applied Behaviour Analysis Act, 2021 is proclaimed, the title “Behaviour Analyst” will be a restricted title that can only be used by individuals registered with the College as Behaviour Analysts. Members registered as Behaviour Analysts may also refer to any earned certification they have, such as a BCBA or BCBA-D certification, that would assist the public in understanding their qualifications as a regulated health provider registered with the College. Non-members who use the title “Behaviour Analyst” or indicate any certification or designation or communicate in any way that could be considered as holding oneself out as a person who is qualified to practice as a Behaviour Analyst, could be in violation of the Act.
Controlled Acts are health care activities or interventions that are considered to be potentially harmful if performed by unqualified persons. Some examples of Controlled Acts are administering a substance by injection, setting a broken bone, dispensing a drug, prescribing glasses, performing a surgical procedure, managing the delivery of a baby, and applying a form of energy. The full list of the 14 Controlled Acts may be found in section 27 of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 (RHPA).
Due to the potential for harm, a Controlled Act may only be performed by a regulated health professional who is authorized, in legislation, to do so. Not all regulated health professions are authorized to perform Controlled Acts. Each profession specific act, e.g., the Medicine Act, 1991, Pharmacy Act, 1991, Psychology Act, 1991, or Nursing Act, 1991, etc., prescribes which, if any, Controlled Acts may be performed by members of that profession.
No. Behaviour Analysts will not be authorized to perform any of the Controlled Acts outlined in the legislation. A Controlled Act may only be performed by those professions that have been granted authorization under the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 and their profession specific acts. The full list of the 14 Controlled Acts may be found in section 27 of the RHPA. This prohibition on performing any of the Controlled Acts is currently in place for individuals practicing applied behaviour analysis or any form of behaviour therapy and will continue with the proclamation of the new Act.
If a Behaviour Analyst registrant is dually registered with another regulatory College, and if their registration with that College qualifies them to perform one or more Controlled Acts, that registrant can continue to perform the Controlled Act(s) they are authorized, in legislation and in their profession specific act, to perform, while engaged in the practice for which they have been authorized to perform the Controlled Act(s).
Many professionals registered with other regulatory colleges, including nurses, social workers, occupational therapists, speech language pathologists, educators, and others, may use behavioural techniques in their practice. As noted above, these will remain in the public domain and are not restricted activities. If, however, a practitioner wishes to use the title “Behaviour Analyst” or indicate any certification or designation or communicate in any way that could be considered as holding themself out as a person who is qualified to practice as a Behaviour Analyst, they will be required to also register with the College of Psychologists and Behaviour Analysts of Ontario.
Dual registration occurs often in many sectors as professionals may hold certificates of registration with more than one regulator to practice multiple professions. It is permissible, and may be necessary, for a Behaviour Analyst to be registered with more than one regulatory College. In this same vein, Psychologists and Psychological Associates, that want to be able to use the restricted title “Behaviour Analyst”, must meet the registration requirements to obtain a second certificate of registration authorizing practice as a Behaviour Analyst.
Professional liability insurance coverage is required for all regulated health professionals. Behaviour Analysts will be required to hold or otherwise be covered by professional liability insurance in all settings in which they practise. Insurance must be in place upon registration and confirmed annually with the College during the annual renewal process.
A Behaviour Analyst who is employed by an organization may be insured under their employer’s professional liability insurance policy so long as it meets the minimum requirements to be set by the College. It is important to know however, that one’s insurance through the workplace covers only the services provided while working for that employer. If an employed Behaviour Analyst also provides services to clients outside of their employment, they must also obtain individual professional liability insurance.
Professional liability insurance can be obtained through associations, insurance companies and other organizations and coverage must be in accordance with the College By-laws.
The College has designed a Self-Screening Tool to assist practitioners of behaviour analysis, therapy, or intervention to determine if they will need to apply to the College once preregistration opens. To view the Self-Screening Tool click here.
The temporary transitional registration routes will close at 11:59pm on June 30, 2026.
Applicants who are in the process of receiving their BCBA or BCBA-D certification with the Behavior Analyst Certification Board are encouraged to complete the requirements for their certification and apply to the College under Transitional Route #1. The transitional routes will close at 11:59pm on June 30, 2026.
Attestors will need to complete the College’s attestation form, which will be available to downloaded from the application portal, or from the College’s website in the ‘Resources’ section.
Applicants are reminded that the attestation must come from an appropriate attestor, which is someone who:
- holds one of the following professional credentials: Board Certified Behaviour Analyst (BCBA or BCBA-D), or a psychologist or psychological associate, registered with the College of Psychologists of Ontario who has expertise in behaviour analysis, and
- Has observed the applicant in their practice and can attest to the applicant’s current experience and competence to practice within the scope of practice of the profession, including clinical decision-making.
Psychological associates/psychologists can only provide services within their competence (i.e. knowledge, skill, and clinical judgement). ABA services can fall within the scope of practice of psychological associates and psychologists and can be considered a “psychological intervention” given the overlap in behavioural competencies. Although there is considerable overlap between the scope of practice of ABA and psychology, these are distinct professions. Psychological associates and psychologists must identify themselves to the public by their psychology title and cannot use the title “Behaviour Analyst” unless dually registered.
Please refer to the chart below for more information.
| Activities | I am a Psychologist/Psychological Associate | I am a Behaviour Analyst |
| I can supervise ABA services of unregistered providers | Yes | Yes |
| I can supervise ABA registrants who are in supervised practice[1] | Depends[2] | Yes |
| I can call myself a
“Behaviour Analyst” |
No | Yes |
| I can supervise autonomous psychologists/psychological associates in ABA services[3] | Yes | Yes |
| I can supervise autonomous Behaviour Analysts in ABA services[4] | Yes | Yes |
| I can perform the controlled act of communication of a diagnosis | Yes | No |
| I can perform the controlled act of psychotherapy | Yes | No |
[1] Supervised practice is the formal period of training required by the College in order to become an autonomous registrant.[2] Psychologists and psychological associates may supervise Behaviour Analysts in supervised practice, but cannot serve as their primary supervisor; this must be a Behaviour Analyst[3] Autonomous psychology members may seek out supervision to expand their practice in particular psychological interventions, including ABA services.[4] Autonomous Behaviour Analysts may seek out supervision from psychology or ABA members, such as when serving new populations and/or in specific ABA techniques.
The College understands that individuals holding these certification levels do not have the requisite education in behaviour analysis at a master’s level or higher, to qualify for either Entry Level registration or registration using Transitional Route #2. In addition, those applying using Transitional Route #2 must provide evidence of competence to practice as a behaviour analyst responsible for independent clinical decision making with respect to client care. According to BACB, individuals holding either RBT or BCaBA certification levels must practice under supervision with respect to client care, and therefore, would not qualify for registration as a Behaviour Analyst under Transitional Route #2.
It is an individual’s decision if they will maintain their BCBA certification. Only individuals who are registered with the College as Behaviour Analysts will be able to use their BCBA credential in Ontario. A BACB certification is necessary for registration in most of the States where ABA is regulated; therefore, maintaining certification provides mobility options to the US.
The BACB recently announced that effective July 1, 2026, “Ontario residents will no longer be able to apply for BCBA certification or take the examination”. Existing BCBA and BCBA-D certified individuals will be able to maintain their certification after July 1, 2026.
On the day the new Act is proclaimed, and going forward, only those who have registered with the College will have access to the restricted title “Behaviour Analyst”. Because it includes the title “Behaviour Analyst”, use of the BCaBA credential post-proclamation will be prohibited in Ontario.
The BACB recently announced that beginning on July 1, 2024, all RBT and BCaBA certificants will have their certificates placed on voluntary inactive status by the BACB. Please contact the BACB directly for information about this change.
Under the Regulated Health Professions Act (RHPA), the use of the title “Doctor” is restricted in Ontario. With the exception of chiropractors, optometrists, physicians, psychologists, and dentists, “no person shall use the title “doctor”, a variation or abbreviation or an equivalent in another language in the course of providing or offering to provide, in Ontario, health care to individuals” (33 (1), RHPA).
Registered Behaviour Analysts will not be allowed to use the title “doctor”, a variation, or abbreviation, while providing or offering to provide services in applied behaviour analysis.
Only Behaviour Analysts who hold a Certificate of Registration Authorizing Autonomous Practice with the College can provide clinical supervision to Behaviour Analysts in Supervised Practice.
Applicants applying for registration as a Behaviour Analyst will be required to obtain a Vulnerable Sector Check. Applicants living in regions that do not issue Vulnerable Sector Checks for registration purposes will be asked to provide a Level 2 Criminal Record and Judicial Matters Check. These applicants will also be required to sign an Undertaking and Agreement with the College.
A Vulnerable Sector Check is the standard police screening for individuals who work with vulnerable persons. A Vulnerable Sector Check collects offense information, including convictions, outstanding warrants, juridical orders, charges, and record suspensions (pardons) for sexual offences.
All applicants for registration as a Behaviour Analyst are required to provide the results of a Vulnerable Sector Check as part of their application. The practice of applied behaviour analysis is used widely to treat autism and other developmental disabilities, and Behaviour Analysts work closely with and have authority over children and other vulnerable persons in their care. A Vulnerable Sector Check provides an added level of public protection by obtaining information from an outside entity about an applicant’s good character.
The College will only accept Vulnerable Sector Checks that were issued within 6 months from the date the College receives it.
To obtain a Vulnerable Sector Check, please contact your local police service for more information. You will be responsible for obtaining the correct type of check and ensuring all related fees are paid. Each police service has different processing times, and it may take time to receive the results of a Vulnerable Sector Check. It is recommended to allow yourself enough time to apply for the Vulnerable Sector Check ahead of your registration date, but no more than 6 months before.
All applicants must upload the original results of the Vulnerable Sector Check to the College through the application portal. Applicants should keep a scanned copy for their records. If the Vulnerable Sector Check is password protected, please email the password to cpo@cpo.on.ca. If your original results were issued as a paper hard copy from the police, please submit them to the College in an enclosed letter:
The College of Psychologists of Ontario
110 Eglinton Ave West, Suite 500
Toronto, ON, M4R 1A3
For applicants living in the City of Toronto, please contact the Toronto Police Service to obtain a Vulnerable Sector Check. The Toronto Police Service offers an online, in-person and mail-in option. Visit the Toronto Police Services website for more information.
A unique “Agency Code/Program Number” code that the College has been assigned by the Toronto Police will be required. The College’s Agency Code/Program Number is: 202311TPSONA3383
If you currently reside outside of Canada and are unable to obtain a Vulnerable Sector Check, please contact the College at aba@cpo.on.ca.
The College maintains a register of all current members. Beginning on July 1, 2024, information about an individual Behaviour Analyst will be available in the searchable Public Register or obtained from the College by telephone 416-961-8817or by e-mail: cpo@cpo.on.ca.
Yes. The College will investigate if you have concerns about services provided under the supervision of a behaviour analyst. However, the investigation will focus on the College member, and not on the supervised. Behaviour analytic services provided under supervision are the supervising member’s responsibility.
The College also investigates misuse of the titles “Doctor,” “”Behaviour Analyst” and any variations on the restricted title. The College also investigates non-members who hold themselves out as qualified to practice as a Behaviour Analyst.
No. The hallmark of self-regulation is a professional’s ability to independently reflect and make ethical decisions in the best interest of their clients. This self-awareness is relevant to practicing within one’s competence, which requires knowledge, skill, and clinical judgment. Registration as a Behaviour Analyst does not imply that one can practice with any client, in any situation, and for any purpose within the scope of applied behaviour analysis. One must know what they know, but as importantly, they must know that they don’t know everything. Awareness of limits of professional competence and taking disciplined steps to practice safely is required of all registrants of the College as indicated by the Standard of Professional Conduct (2017) which states:
5.1 Practising Within Areas of Competence
Members may only provide services within their authorized areas of practice and with their authorized client populations, and then only when competent to provide those particular services.
Members wishing to provide services that are beyond their competence but are within their authorized areas of practice and with their authorized client populations may only do so under the professional guidance of a member who is authorized and competent to provide the services being delivered.
Becoming a Member - Psychologists and Psychological Associates
Applicants should review the College’s Registration Guidelines prior to making an application for registration. The College also has Flowcharts which illustrate the different registration pathways:
- Registration Flowchart: Psychologist – Educated in Canada or the USA
- Registration Flowchart: Psychological Associate – Educated in Canada or the USA
- Registration Flowchart: Psychologist – Educated Outside Canada or the USA
- Registration Flowchart: Psychological Associate – Educated Outside Canada or the USA
Guidelines can be found here:
- Registration Guidelines: Psychologist – Supervised Practice
- Registration Guidelines: Psychological Associate – Supervised Practice
If you are unsure about which application route is applicable for you take our How to Apply quiz here.
There isn’t a deadline for receipt of Supervised Practice or Interim Autonomous Practice applications. Applications are reviewed on an on-going basis throughout the year. Once the College has received your completed application form, the application fee, and all supporting documentation, your application is ready for review. The review process is usually completed in four to six weeks.
Once the College has received your completed application form, the application fee, and all supporting documentation, your application is ready for review. The review process is usually completed in four to six weeks (up to 30 business days).
After the review, if the Registrar has any doubts or concerns about your meeting the academic or good character requirements, or about your training in your proposed area(s) of practice, your application is referred to the Registration Committee for further review. You will be notified of this referral and given 30 days to submit any further information to assist the Registration Committee in its review. The Registration Committee meets about every six weeks throughout the year. The application review will be scheduled for the next available meeting after the 30-day notice period.
Once the review of your application is complete, you will receive a letter confirming the outcome.
Applicants are encouraged to submit their completed application form and supporting documentation as soon as possible. You can track the status of your application using the Checklist feature in your on-line application. This Checklist will tell you which documents have been received and which are outstanding. If you have questions about the status of your application, you can email your questions using the same on-line application portal.
Any supporting documentation that arrives at the College before your application will be filed according to your name. Once your application arrives, the supporting documentation will be included with it.
Once the College receives your application and fee, you have 24 months to submit all the supporting documentation. The application will expire after 24 months unless a certificate of registration or a confirmation of eligibility has been issued. At this point, the application and all supporting documents will be destroyed. The application fee is non-refundable.
The College will accept a pre-convocation transcript in order to review your application if you have completed all requirements for your degree but have not yet convocated. The transcript must be accompanied by a signed letter from the Senate or Registrar of the University or an appropriate Department of Psychology designate such as the Director of Clinical Training. The letter must confirm the date that your degree requirements were successfully completed. The letter must be submitted to the College directly from the University. The College will not accept a student copy of the letter. Universities may send official electronic letters directly to cpo@cpo.on.ca.
No. The College will only accept academic transcripts sent to the College directly from a University. It is your responsibility to contact the University and ask them to send a copy of the official academic transcript directly to the College. Universities may send official electronic transcripts directly to cpo@cpo.on.ca.
The College will approve the start date for supervised practice based upon the date that both your Primary and Alternate Supervisors confirm that their supervision of your work began,
or
the date that the last supporting document for your application was received, whichever date is later.
No. You can apply for supervised practice, even if you are not yet working in Ontario. You should submit the application form, including the fee and supporting documentation. The College understands that you will not be able to complete the section titled “Authorized Supervised Practice” and the Primary and Alternate Supervisors’ Agreement Forms.
The College will proceed to evaluate your academic credentials. If your application is found to be acceptable, the Registrar will wait to issue you the certificate for supervised practice until you have found an appropriate work setting and named two supervisors.
In the meantime, if your application is approved, you can choose to take the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology (EPPP) and the Jurisprudence and Ethics Examination (JEE).
Yes. Supervised practice is intended to prepare you to practice psychology in Ontario. It must be completed here under the College’s Standards of Professional Conduct and Ontario legislation. The College’s mandate is to protect the public of Ontario. Psychological services provided in another province or state follow the rules of the regulatory board for psychology in that province or state only.
You are responsible for finding a suitable job as well as your Primary and Alternate Supervisors. Generally, once you find a job, your employer will have a member(s) of the College on site or who consults to the organization who can supervise your work. The College’s online Public Register (www.cpo.on.ca), may be of assistance in your search for supervisors. The Ontario Psychological Association (www.psych.on.ca) provides a listing of its members who may be available to provide supervision.
The application fee may be paid by credit card on the online application site.
The College does not accept applications by email or fax. Please use the online application site.
You may receive a copy of all information and each document that the College has that is relevant to your application. Please note that the College does not return original documents however, you may ask for a copy of the documents in your registration file.
To obtain a copy of your registration file you must makea written request to the College either in-person, by mail, or by e-mail. There is a charge of 20¢ per page for this. Upon receiving the written request, registration staff will determine the number of pages in the record and advise you of the cost before proceeding.
In the meantime, if your academic credentials are approved, you may take the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology (EPPP) and the Jurisprudence and Ethics Examination (JEE).
To include families on your Declaration of Competence, you must be engaged in family assessment and family intervention during your supervised practice period. In such cases, the family would be the primary client. If however, you will not be providing direct services to families, but instead will see parents or families in the context of your work with the children or adolescents within the family, then it is not appropriate to indicate families on your Declaration of Competence. The College recognizes that working with children and adolescents as declared client groups often involves meetings with parents or families. It is important to distinguish between families as a specific client group with whom one works, and family involvement in the context of working with the children or adolescents in the family.
The Registration Committee is a statutory committee under the Health Professions Procedural Code. In accordance with the By-laws, the Registration Committee is composed of at least three members of the Council who are members of the College, at least two public members of the Council, and at least two members of the College who are not members of the Council.
Under the Code, if an applicant meets the qualifications and requirements, the Registrar may issue a certificate of registration. However, if the applicant does not meet the qualifications and requirements, the Registrar refers the application to the Registration Committee for a determination. It is then the duty of a panel of the Registration Committee to determine the eligibility of the applicant for a certificate of registration. In addition, applicants may be referred to the Registration Committee for advice and recommendations as to how they can bring themselves to meet the registration requirements and to acquire and demonstrate the knowledge and skills required for their declared area of competence.
The Committee is divided into two panels. One Co-Chair of the Committee serves on each of the panels. The Registration Committee meets approximately every other month. For the convenience of applicants wishing to submit information to the Committee, meeting dates are posted on the College’s website. Submissions must be received 10 days in advance of a meeting.
Should you have any questions or concerns about a Registration Committee decision, you may contact the College directly to speak with a Registration Assistant, or you may e-mail the College at registration@cpo.on.ca
If you disagree with a decision of the Registration Committee you have the right to appeal the decision to the Health Professions Appeal and Review Board (HPARB).
You must write directly to HPARB within 30 days of receiving the Registration Committee’s decision letter.
HPARB may be contacted at the address below:
Health Professions Appeal and Review Board
151 Bloor Street West, 9th Floor
Toronto, ON, M5S 1S4
Telephone: 416-327-8512
Toll Free: 1-866-282-2179
TTY/TDD: 416-326-7TTY or 416-326-7889 1-877-301-0TTY or 1-877-301-0889
Fax: 416-327-8524
E-mail: hparb@ontario.ca
Website: www.hparb.on.ca
Ontario Regulation 74/15 - Registration
The new regulation (O. Reg. 74/15) replaces O. Reg. 533/98 and revises and updates the requirements for registration with the College. The new regulation reflects changes that were approved by Council and submitted to the Ontario government for approval in October 2013.
The revised Registration Regulation became effective on April 7, 2015.
The most significant changes are that:
- The new regulation is more specific about the graduate psychology training requirements for registration as a Psychologist and as a Psychological Associate. Whereas the old regulation indicated that an applicant had to have completed a degree from “a program of study with content that is primarily psychological in nature as required in the guidelines published by the College”, the new regulation indicates that a Psychologist applicant must have a doctoral degree from a CPA-accredited or equivalent psychology program. The specific curriculum content of acceptable psychology programs for master’s level Psychological Associate registration is also now outlined in the regulation.
- Other requirements previously outlined in the guidelines, such as those regarding supervised practice, are now specified in the regulation.
- The examinations (EPPP, JEE, and Oral Exam) applicants must pass as a requirement of registration are now specified in the regulation.
- The new regulation eliminates the “status” of certificates for Inactive, Retired, and Academic registration; these will now become classes of certificates of registration. This does not change the conditions for holding these certificates.
- Any applicant whose completed application to the College is received on or after April 7, 2015, will need to meet the requirements as outlined in the new regulation.
- Applicants who applied and whose required documentation to complete their application for review by the College had been received by the College prior to April 7, 2015, will be processed under the previous (old) regulation
- Applicants who applied and whose required documentation to complete their application for review by the College had not been received prior to April 7, 2015, will be notified that once they complete their application it will be processed under the new regulation.
Yes – such applicants will now be required to pass the College’s Jurisprudence and Ethics Examination (JEE) as a requirement for obtaining a Certificate of Registration for Autonomous Practice. Qualified applicants will initially be able to register for and hold a Certificate for Interim Autonomous Practice for up to 12 months, which will enable them to practise while they prepare for and write the JEE.
For more information, please feel free to contact the College at cpo@cpo.on.ca if have any questions
Registration Examinations in Psychology
Once your application for registration has been approved by the College, you will be provided with details on how to register to take the EPPP and the JEE. While you do not need to hold a certificate authorizing supervised practice in order to be eligible to take these examinations; your application for registration must have been approved by the College.
The EPPP is a computer based multiple choice examination and is available throughout the year at various designated computer testing centres throughout Canada and the United States.
The JEE is a multiple-choice examination offered on-line two times per year – each Spring and each Fall. Upcoming JEE dates are posted on the College’s website here.
Supervised practice members must, in order to remain in good standing, take the EPPP and the JEE within one year of issuance of the certificate for supervised practice.
You may take the EPPP and the JEE in any order that you prefer.
The oral examination is the last step in the registration process. To be invited to attend an oral examination, you must have passed the EPPP and JEE and fulfilled all other requirements, including the period of authorized supervised practice.
No. College staff are not permitted to convey exam results over the telephone, fax or via e-mail. Exam results are only sent to candidates via mail. JEE results are mailed out approximately 6 weeks following the examination, and EPPP results are mailed out approximately 4 weeks following an examination. If you are concerned because you have not yet received your exam results, please contact the College to enquire whether your score has been mailed out to you yet.
Once your application for registration has been approved by the College, you will be provided with details on how to register to take the EPPP and the JEE.
The College does not recommend any particular method of preparation for the EPPP. Some candidates find materials published by commercial examination study companies to be helpful, but these commercial study materials are not endorsed by the College. Information on how to prepare for the EPPP, including a computer based practice exam, can be found on the website of the Association of State and Provincial Psychology Boards (ASPPB) at www.asppb.net.
Applicants who took the EPPP as part of the registration/licensure requirements in another jurisdiction, and who received a scaled score of at least 500 or a percentage score of at least 70% are not required to re-take this examination.
Please arrange to have your EPPP results forwarded directly to the College of Psychologists of Ontario by contacting the Association of State and Provincial Psychology Boards (ASPPB) at the following link: http://www.asppb.net/?page=ScoreTransfer
The College recommends that candidates review the preparatory information outlined in the document titled Preparing to take the Jurisprudence and Ethics Examination.
As well as the list of relevant Legislation and Standards
Additionally, detailed information about the JEE including (but not limited to) an Examination Blueprint of the content of the examination, pass point and scoring, number of attempts permitted, and exam accommodations is outlined in the Examinations section of the Registration Guidelines: Supervised Practice:
Psychological Associates’ Exams
The Supervision Resource Manual also includes some information on how candidates can prepare to take the JEE.
Candidates generally perform very well on the JEE. Ontario-educated candidates tend to do better than those candidates who did not receive their education in Ontario.
The pass rate on the JEE over the past 11 years has been 89%. Only 6% of candidates have scored under 60%. The cut-score is generally about 66%, ranging from 62% to 69% for any one particular administration of the JEE. The highest score on each individual exam ranges from 86% to 98% and the lowest score ranges from 35% to 65%. The average score for the JEE over the past 11 years is 76%.
Of particular note is that the pass rate observed on the JEE, both for Ontario educated and internationally educated candidates, is comparable to that of other high stakes professional licensing examinations.
Internationally educated candidates are a very diverse group from many different countries. Many factors affect their success on the JEE, including language of education and language of clinical practice, years since graduation, and practice patterns in the country of education, that is, whether they are similar to Canada or different.
Familiarity with the exam format may also affect the pass rate. In other words, candidates who have experienced multiple-choice exams during their education program may perform better than those candidates who have not experienced multiple-choice exams.
The leading psychometric standard-setting body, the American Educational Research Association (AERA), specifically recommends that professional licensing examinations not use a “norm-reference approach” – that is, adjusting an examination’s pass rate so that a specified percentage of candidates pass each time. Standard 11.16 says
“The level of performance required for passing a credentialing test should depend on the knowledge and skills necessary for credential-worthy performance in the occupation or profession and should not be adjusted to control the number or proportion of persons passing the test.”
American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, National Council on Measurement in Education. (2014). Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington DC: American Educational Research Association.
You can expect to receive your JEE score approximately 6 weeks after taking the examination.
It takes approximately 1-2 weeks to record and verify all candidate’s scores. Then, the Jurisprudence and Ethics Examination Committee (JEEC) begins the process of psychometric analysis of items and setting the passpoint for that particular examination. The Registration Guidelines outline the procedure used by the JEEC to set the passpoint. This process takes approximately 1-2 weeks to be completed.
Once the exam passpoint has been set and individual results have been verified, College staff prepare each candidate’s notification for mail out and this process takes approximately 1-2 weeks to be completed.
College staff are not permitted to convey exam results over the telephone, fax, or via e-mail.
The College does not provide feedback regarding a candidate’s performance within specific areas of the blueprint of the JEE or make recommendations for remediation. Only the total score that the candidate achieved is provided, along with the cut-score, mean, and standard deviation.
The JEE is a professional licensing exam. Professional licensing exams are used to evaluate knowledge, skills, and abilities (i.e. competence) required to practise a profession at an entry-level, in the interest of the protection of the public. These types of examinations are not designed or intended to provide feedback to candidates. In this case, the JEE is used to evaluate knowledge of jurisprudence, ethics, and standards related to the practice of psychology in Ontario.
The reliability of the results of any exam is strongly related to the number of items (questions) on the exam. Similarly, the reliability of any information provided to candidates related to scales within the exam is related to the number of items within that scale. Given the JEE Examination Blueprint (as outlined in the Registration Guidelines), some categories may have as few as four to seven items. When there is a small number of items in a scale the reliability and also validity of any report based on these scales would be questionable as feedback to the candidate.
The Registration Guidelines: Supervised Practice (psychologist) and Registration Guidelines: Supervised Practice (psychological associate), describe the oral examination, and the Supervision Resource Manual provides information on how candidates should prepare for the oral examination.
Candidates who have special requirements arising from documented impairments or disabilities may request accommodations in taking any of the College’s required examinations.
The College’s Examination Accommodation Policy is found in the Registration Guidelines, and the forms required for requesting an accommodation are found in the application for registration.
If you have a question about requesting an examination accommodation you may contact exams@cpo.on.ca for assistance.
The forms required for requesting an examination accommodation are found in either the application for supervised practice or the application for interim autonomous practice. How to Apply
If you have a question about completing the examination accommodation forms you may contact exams@cpo.on.ca for assistance.
You may submit your request for an examination accommodation at the same time that you apply for registration with the College or you may submit your request later if necessary.
In all cases, the College’s examination accommodation request form, and documentation, either from your regulated health care professional or the university from which you graduated, must be submitted to the College at least 60 calendar days in advance of an examination administration in order to allow sufficient time for your request to be reviewed and for accommodations to be arranged.
Exam candidates requesting accommodation will be advised of the College’s decision within ten (10) business days of the submission date, unless more information is needed to effectively evaluate the accommodation request.
A candidate who has applied and has been granted examination accommodation for a permanent or long-term disability will not be required to re-apply for accommodation for subsequent attempts but must confirm to the College that accommodations are still required.
If the request was related to a temporary condition (e.g. recent injury or pregnancy-related conditions) or if five years have passed since the initial accommodation request, the College may request updated information confirming the continued need for accommodation.
When re-applying to take the JEE, the College’s JEE Registration Form will require you to indicate whether you need accommodations, and if so to indicate whether you have already submitted the necessary accommodation request form.
When re-applying to take the EPPP, the ASPPB’s candidate request form will require you to indicate whether you need accommodations.
If the accommodation that you require has changed in any way from what was previously granted, you may be required to re-apply. Please contact exams@cpo.on.ca for assistance.
Psychology Applicants Educated Outside Canada or the USA
Yes, you can begin the application process before arriving in Canada. The Registration Guidelines outline the steps in the registration process that may be completed before moving to Canada
Registration Guidelines: Registration Process – Psychologist
Registration Guidelines: Registration Process – Psychological Associate
If your degrees are from a university outside of Canada or the United States they must be evaluated to determine if they are comparable in level to a degree from a Canadian university. This evaluation may be arranged through either World Education Services (WES) www.wes.org/ca or Comparative Education Service (CES) https://learn.utoronto.ca/comparative-education-service.
This evaluation must demonstrate that your highest degree in psychology is at either the masters or doctoral level. While the statement from WES or CES will indicate to the College whether the academic credentials are comparable in level to either a master’s or doctoral degree granted by a Canadian university, the College reserves the right to make a final determination of the level and will evaluate, in accordance with the guidelines to determine, whether the content of the degree(s) is primarily psychological in nature.
Educated Outside of Canada/USA / Evaluation of Academic Credentials
If your transcript and official university documents are in a language other than English or French, you must arrange to have these documents translated by an official translator. Applicants are responsible for any fees associated with the translation of their documents.
If a university outside Canada or the U.S. is unable to send a transcript directly to the College, the College may accept a certified copy of the transcript the university issued to the applicant.
No. You may submit an application for supervised practice along with all the supporting documentation, including the application fee, with the exception of the section of the application form titled “Authorized Supervised Practice” and the primary and alternate supervisors’ agreement forms. Your academic credentials will be reviewed but further consideration of your application will be deferred until you have found suitable employment and supervisors.
In the meantime, if your credentials are approved, you can take the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology (EPPP) and the Jurisprudence and Ethics Examination (JEE).
No. It is acceptable for post-master’s work experience to be completed outside of Ontario or Canada.
The steps in the registration process are outlined in detail in the Registration Guidelines, however, a flowchart illustrating the steps in the registration process for applicants whose degrees are from outside of Canada and USA is also available in the “Applicants” section of the College’s website. There is a flow chart for Psychological Associate applicants and a flow chart for Psychologist applicants. You can find the flowcharts here:
You are responsible for finding a suitable job as well as your Primary and Alternate Supervisors. Generally, once you find a job, your employer will have a member(s) of the College on site or who consults to the organization who can supervise your work. The College’s online Public Register (www.cpo.on.ca), may be of assistance in your search for supervisors. The Ontario Psychological Association (www.psych.on.ca) provides a listing of its members who may be available to provide supervision.
You may receive a copy of all information and each document that the College has that is relevant to your application. Please note that the College does not return original documents however, you may ask for a copy of the documents in your registration file.
To obtain a copy of your registration file you must makea written request to the College either in-person, by mail, or by e-mail. There is a charge of 20¢ per page for this. Upon receiving the written request, registration staff will determine the number of pages in the record and advise you of the cost before proceeding.
In the meantime, if your academic credentials are approved, you may take the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology (EPPP) and the Jurisprudence and Ethics Examination (JEE).
Complaints & Reports - General
Complaints and reports are different ways of letting the College know about your concerns. There are several key differences between a complaint and a report:
| Investigation | Complaint / Reporter Involvement |
Timelines | Review | |
| Complaint | The ICRC must investigate every complaint it receives.* | The complainant:
|
150 days. The College can extend this timeline | The complainant and member may ask the Health Professions Review Board (HPARB) to review the ICRC’s decision. |
| Report | Not every report is investigated. The Registrar decides what to do with each report on a case-by-case basis | A report:
|
There is no set time for investigating a report. | HPARB cannot review the ICRC decision. |
Anyone who has a concern about a psychologist or psychological associate can file a complaint or submit a report. This includes a client, a family member, or friend of the client, an employer, an insurer, a colleague, or a general member of the public.
Clients do not have to make a complaint or report. However, some people, in some situations, do have to make a Mandatory Report. For more information, please click here.
You do not have to be involved in the College’s investigation. The College will still conduct a full investigation of your complaint and give you a copy of the decision.
Yes. Please see additional information about the College’s facilitated resolution process.
The College has a strict duty of confidentiality. It will not share your information with anyone outside of the ICRC investigation. However, on some occasions, the information may become public:
Referral to the Discipline Committee: Discipline hearings are public. However, the Discipline Committee can ban the publication of information that could identify you.
HPARB review: The College must give its investigation record to HPARB. HPARB also holds public hearings. HPARB is independent of the College and has its own processes. You may contact HPARB directly should you have any questions.
Complainants may find it helpful to have a lawyer, but it is not necessary. Most complainants proceed without a lawyer.
Members often do use lawyers when responding to complaints or reports. This is because the process may have a significant impact on the member’s practice and career.
The role of the College is to protect the public from harm. The College does so by setting and upholding rules and Standards for its members. These rules and Standards address many different concerns, including:
- Boundaries and sexual abuse;
- Appropriateness of services;
- Supervision;
- Fees and billing;
- Confidentiality and disclosure of information.
The College’s standards and rules cover most of the concerns brought to the College’s attention. Please contact the College if you are not sure whether your concerns are covered.
No. The College cannot get involved in fee arrangements or make financial awards.
No. The College only has jurisdiction over individual members.
Yes. The College will investigate if you have concerns about services provided under the supervision of a psychologist or psychological associate. Psychological services provided under supervision are the supervising member’s responsibility. However, the investigation will focus on the College member, and not on the supervised.
The College also investigates misuse of the titles “Doctor,” “psychologist” and “psychological associate.” The College also investigates non-members who imply that they can provide psychological services.
The College will try to direct you to another body that may be able to address your concerns.
No, the College cannot process anonymous complaints. The College shares your name and concerns with the member as part of its investigation. However, the College can block out irrelevant information, such as personal contact information.
If you want to provide information to the College without filing a complaint, you can make an anonymous report. However, depending on the information you provide, the College may be limited in its ability to investigate.
Please see the FAQ about the difference between complaints and reports.
No, there is no time limit for filing a complaint. However, the College recommends that you raise your concerns as soon as possible. The earlier a complaint or report is received, the fewer problems may arise with the investigation. For example, it is more likely that relevant documents will still exist and witnesses can be located.
Mandatory reports have specific timelines attached. Please see the FAQs about mandatory reports.
Complaints & Reports - Filing a Complaint or Report
You can submit a complaint or report to the College through electronic forms. You may also submit a complaint or report in writing or other recorded format, including film and audio. These can be sent directly to the College by email, fax, or regular mail.
You should provide as many details about your concerns as possible. Supporting documents such as emails, reports or bills are also helpful. You may also provide the names of relevant witnesses.
You may search for a member on the College’s Public Register. Please contact the College staff if you have trouble identifying the member.
You can request to withdraw your complaint. The Registrar or the ICRC will review your complaint and request. If your concerns are serious, the Registrar or ICRC may still decide to continue with the investigation.
Complaints & Reports - Investigations
The College must investigate every complaint, with limited exceptions. The College will not investigate a complaint that is “frivolous, vexatious, made in bad faith, moot or an abuse of process.”
This can happen when the complaint is about something that happened before the professional was a member of the College. Another example is where the conduct is private and does not relate to the member’s professional practice.
The College will notify you and the member if it decides not to investigate. You will have a chance to respond to that decision before it becomes final. Once it is final you may ask that HPARB review that decision.
Your complaint will be assigned to a Case Manager, who will manage the complaint file. The Case Manager will be your contact person at the College and is available to answer your questions.
The College will send your complaint to the member. The member will have a chance to review the complaint and respond. In most cases, the College will request that the member provide the clinical record. At the same time, the College will acknowledge your complaint in writing.
The Case Manager will also conduct further investigation. This can include interviewing witnesses and getting other documents.
When the investigation is complete, the complaint file will go to a panel of the ICRC.
Let the case manager know which information you want to access. The College may be able to get that information by way of summons.
The legislation requires the College to complete investigations within 150 days. However, this is not always possible. The legislation also allows the College to extend this timeline, with notification to the complainant and member.
The Inquiries, Complaints and Reports Committee, or ICRC, is responsible for decisions about complaints.
A panel of the ICRC will review your complaint and make a decision about how to proceed. Every panel includes one public and two professional members of the Committee.
The ICRC is a screening committee. It cannot make findings of fact or credibility. The role of the ICRC is to decide how to best protect the public from possible harm.
For every complaint, the ICRC considers the possible risks of the member’s conduct to the public. The ICRC considers both impact and recurrence risks. If the risks are low, the ICRC may decide not to take any action. If the risks are moderate or high, the ICRC is likely to take some kind of action.
The ICRC has developed a table to help with its consideration of risks. This table is available here.
The ICRC meets in person every month from September to May. The ICRC attempts to meet twice over the summer months.
The ICRC also meets by teleconference throughout the year.
The College will send you a formal acknowledgment of your complaint within 14 days of receiving your complaint.
The Case Manager assigned to your complaint will be in touch with you directly if they need additional information.
If the College is unable to meet the 150-day timeline, the College will let you know. The College will then set new timelines.
The College will send you a copy of the ICRC’s decision once it is finalized.
A panel of the ICRC might not come to a final decision when they consider a complaint. The panel may have some questions for one of the parties or may want more information. They will then need to meet again to reach a decision.
The panel also needs some time to write the decision. College staff is not able to communicate any information about an unfinished decision.
No. The ICRC does not meet with either the complainant or the member. The ICRC reviews information contained in paper or electronic records.
Complaints & Reports - ICRC Decisions
No. Only the Discipline Committee can make a finding of professional misconduct after a hearing.
The ICRC can decide whether to refer allegations to the Discipline Committee. If it does not make a referral, the ICRC can still express concern about conduct and take some action.
The action the ICRC takes will depend on the risks associated with the member’s conduct. Please see more information about the ICRC Risk Assessment Framework.
The ICRC may take a range of actions after an investigation:
-
No further action: A panel may take no further action if it believes there is no risk to the public.
-
Advice: A panel may give advice if it identifies low risks. Advice is meant to help the member avoid future risks.
-
Undertakings: A panel may ask for an undertaking from the member if it identifies moderate risks. An undertaking is remedial and is agreed to by the member. An undertaking can range from a minor change in practice to limitations on the member’s certificate of registration.
-
Caution: A panel may caution a member if it identifies moderate risks. The member must come to the College to receive the caution in person. Cautions are remedial and may include a discussion between the panel and the member. Cautions are not open to the public.
-
Specified Continuing Education or Remediation Program (SCERP): A panel can order a SCERP if it identifies moderate risks. A SCERP is remedial and can include a specific course of study.
-
Referral to the Discipline Committee: If the ICRC identifies high risks, it will refer the matter to the Discipline Committee for a full hearing.
- Referral to a Health Inquiry or Fitness to Practice Committee: Sometimes the ICRC identifies health issues that could affect the member’s ability to practice. In these cases, the panel will refer the matter to a Health Inquiry panel of the ICRC. A Health Inquiry panel can order treatment and monitoring. If treatment and monitoring are not enough to ensure safe practice, the ICRC may refer the matter to the Fitness to Practice Committee.
In the last 5 years (January 2015 to March 2020), ICRC outcomes in relation to 416 cases were as follows:
| Outcome | Number* | Percentage* |
| Withdrawal/closed | 10 | 2% |
| Take No Further Action – F&V † | 55 | 13% |
| Take No Further Action | 157 | 38% |
| Advice | 85 | 20% |
| Written Caution ‡ | 37 | 9% |
| Caution | 17 | 4% |
| Undertakings | 41 | 10% |
| SCERP | 17 | 4% |
| Refer to Discipline Committee | 18 | 4% |
| Total | 437 | 105% |
*The Percentages add up to more than 100% due to multiple outcomes in some cases, i.e. caution and undertaking. The 437 outcomes here relate to 41 cases.
† Frivolous, vexations, made in bad faith, moot, or an abuse of process. See the FAQs above.
‡ As of September 8, 2017, the ICRC no longer issues written cautions.
The College is required to post specific information on the Public Register. The College will not post any information that could identify the complainant or client. Information posted on the Public Register includes:
- A notation and synopsis of any undertaking, while it is in effect;
- A notation of any caution;
- A notation of any Specified Continuing Education or Remediation Program (SCERP);
- A notation of every matter referred to the Discipline Committee;
- The specific allegations referred to the Discipline Committee;
- The result of every Discipline proceeding;
- The result of every Fitness to Practice proceeding;
- Information about a member’s criminal charges or convictions; and
- Information about any interim order that may be in effect.
In most cases, you and the member can ask that the Health Professions Appeal and Review Board (HPARB) review the ICRC’s decision. HPARB cannot review referrals to the Discipline or Fitness to Practice Committees. There are not final decisions but rather involve other College processes.
In a review, HPARB will consider whether the College’s investigation was adequate. It will also consider whether the decision was reasonable. The College sends instructions on how to ask for a review with your copy of the ICRC decision.
No. Section 36(3) of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 does not allow information from a College proceeding to be used in civil court.
Complaints & Reports - Mandatory Reports
The timelines are set out in the Health Professions Procedural Code, 1991, which is section two of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 as follows:
Timing of report
(2) The report must be filed within 30 days after the obligation to report arises unless the person who is required to file the report has reasonable grounds to believe that the member will continue to sexually abuse the patient or will sexually abuse other patients, or that the incompetence or the incapacity of the member is likely to expose a patient to harm or injury and there is urgent need for intervention, in which case the report must be filed forthwith. 2007, c. 10, Sched. M, s. 62 (1).
A report must be filed in writing. Please use the College’s <a href=”https://members.cpo.on.ca/public_register/mandatory_report_form”>mandatory report form</a> available on the College’s website. You may also write to the College directly through <a href=”https://cpo.on.ca/contact-us/”>fax, mail or email</a>.
The mandatory reporting form will prompt you for the information necessary with respect to each report. If you have any additional questions about your report, please contact the College at 416-961-8817/1-800-489-8388; or invhear@cpo.on.ca
It may be that your mandatory obligation to report sexual abuse arises in the course of providing psychotherapy to another regulated health professional. In this case, your report must also contain your opinion, if you are able to form one, as to whether this member is likely to sexually abuse patients in the future.
The Inquiries, Complaints, and Reports Committee (ICRC) decides what to do in each case by thinking about the possible negative outcomes of the member’s conduct. The ICRC thinks about this in terms of “risk.”
The ICRC considers both impact and recurrence risks. Impact risks include those to specific individuals, the general public, and the profession. Recurrence risks include concerns about the member’s conduct history, the practices, processes, or systems the member has in place, and the member’s awareness of the practice concerns identified.
The ICRC uses the ICRC Risk Assessment Framework, below, to help categorize these risks. The Framework also helps the ICRC identify the range of appropriate outcomes in relation to the risks.
The outcomes available to the ICRC after the investigation of a complaint or report include:
- No further action: A panel may decide to take no further action if it decides that the member’s conduct poses no risk to the public.
- Advice: A panel may give advice if it identifies low risks. Advice is meant to help the member avoid future risks.
- Undertaking: A panel may ask for an undertaking from the member if it identifies moderate risks. An undertaking is remedial and can range from a minor change in practice to having a mentor.
- Caution: A panel may caution a member if it identifies moderate risks. The member must come to the College to receive the caution in person. Cautions are remedial and may include a discussion between the panel and the member. Cautions are not open to the public.
- Specified Continuing Education or Remediation Program (SCERP): A panel can order a SCERP if it identifies moderate risks. A SCERP is remedial and can include a specific course of study.
- Referral to the Discipline Committee: If the ICRC identifies high risks, it may refer the matter to the Discipline Committee for a full hearing.
COVID-19
Originally published in Volume 2 Issue 1 of HeadLines.
Throughout the pandemic, members have been permitted to use their professional judgment to decide when it was necessary to see clients in-person. The College wishes to advise members that Ontario’s Chief Medical Officer of Health recently rescinded Directive #2 for Health Care Providers (Regulated Health Professionals or Persons who operate a Group Practice of Regulated Health Professionals).This Directive had been amended and re-issued in mid-April due to the increasing COVID-19 case counts, hospitalizations, and ICU admissions. Rescinding of Directive #2 means that non-urgent and non-emergent procedures may be gradually resumed by health care providers and health care entities who were subject to that Directive. This includes in-person services that are non-essential or non-emergent.
In making this decision, the Chief Medical Officer of Health advised that all health care providers should continue to follow the guidance issued by the Ministry of Health in the COVID-19 Operational Requirements: Health Sector Restart. College members are advised to review this document to ensure an understanding of relevant requirements to return to in-person service provision appropriately and gradually.
In returning to the provision of in-person services, the College urges members to take a conservative approach to minimize the risk of community spread as much as reasonably possible, particularly with the emergence of new variants of the virus and localized outbreaks.
Proof of Vaccination:
Some members have asked whether they may require clients wishing to receive in-person services to demonstrate that they have been vaccinated. The Ontario Human Rights Commission has published a document entitled COVID-19 and Ontario’s Human Rights Code – Questions and Answers to provide some guidance to individuals, practitioners and employers. The following section from this document may be of assistance. Please note that this is the published position of the Ontario Human Rights Commission and the College is not qualified or authorized to offer interpretation of the Ontario Human Rights Code. Members seeking specific guidance or further clarity on how to interpret their own responsibilities under the Code are encouraged to seek independent legal advice.
Ontario Human Rights Commission
21. Can my employer or any service or housing provider require proof that I’ve received a COVID-19 vaccine?
- Receiving a COVID-19 vaccine is voluntary.
- At the same time, the government of Ontario has said they plan to issue proof-of-vaccination cards to people who receive a COVID-19 vaccine who may be required to take part in some activities.
- Requiring proof of vaccination to ensure fitness to safely perform work, or protect people receiving services or living in congregate housing, may be permissible under the Code if the requirement is made in good faith and is reasonably necessary for reasons related to safety.
- The Code grounds of disability and / or creed may be engaged when employers, housing or other service providers impose medical testing or treatment requirements, including proof of vaccination.
- Under the Code, organizations have a duty to accommodate people who may be unable to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, for reasons related to disability or creed, unless it would amount to undue hardship based on cost or health and safety.
- The right to be free from discrimination can be limited under the Code, where, for example, broader health and safety risks are serious, like in a pandemic, and would amount to undue hardship. The OHRC and relevant human rights laws like the Code recognize the importance of balancing people’s right to non-discrimination and civil liberties with public health and safety, including the need to address evidence-based risks and treatment associated with COVID-19.
- Everyone involved should be flexible in exploring whether accommodation is possible, including alternative ways a person might continue to safely work, receive a service or live in congregate housing without being vaccinated.
- Organizations should make clear the reasons why proof of vaccination is needed in the circumstances, and ensure prior, informed consent.
- Organizations should only request and share medical information, including proof of vaccination, in a way that intrudes as little as possible on a person’s privacy, and does not go beyond what is necessary to ensure fitness to safely perform work, or protect people receiving services or living in congregate housing, and accommodate any individual needs.
- No one should experience harassment or other discriminatory treatment based on a Code ground because they are unable to receive a vaccine.
- In addition, workers have rights and employers have obligations for workers’ health and safety under the Occupational Health and Safety Act. Visit the Ontario Ministry of Labour, Training and Skills Development website for more information, including how to contact the Ministry.
The College will continue to provide updates to members as further information becomes available.
Please be advised that provisions made for service provided during the pandemic are no longer available as of May 15, 2023. If you have a question about providing psychological services to an existing client who is temporarily in Ontario, please review the College’s information regarding temporary and time limited registration found here
Ontario has recently mandated that individuals must be vaccinated before entering specified high-risk settings. These settings are listed in O. Reg. 364/20: Rules for Areas at Step 3 and at the Roadmap Exit Step under the Reopening Ontario Act, 2020. It appears that this requirement does not apply with respect to entering a place for the purpose of health care.
The Ontario Human Rights Commission recently published a policy statement which provides guidance with respect to COVID-19 vaccine mandates and proof of vaccine certificates. It states, among other important things, that:
While receiving a COVID-19 vaccine remains voluntary, the OHRC takes the position that mandating and requiring proof of vaccination to protect people at work or when receiving services is generally permissible under the Human Rights Code (Code) as long as protections are put in place to make sure people who are unable to be vaccinated for Code-related reasons are reasonably accommodated. This applies to all organizations.
Members considering implementing such policies may find useful information about how to proceed in the Ministry of Health’s Proof of Vaccination Guidance for Businesses and Organizations under the Reopening Ontario Act, Version 2, September 27, 2021. If additional information is required, members may wish to seek independent legal advice.
It is our understanding that the criteria for an official “medical vaccination exemption” are very narrow and that these do not include psychological reasons. As well, only a physician, registered nurse or nurse practitioner may certify such an exemption for settings mandated to require proof of vaccination. It does not appear that members of the College of Psychologists are authorized to provide such certification. It is important that a client making a request of this type be aware of the limits of the member’s authority. Further information may be found in the Ministry of Health’s Questions and Answers, Version 2, September 28, 2021.
If the business or organization is not covered by the mandatory vaccination legislation, members could provide a professional opinion concerning a client’s need for accommodation. In doing so, as with any professional opinion given, they must be prepared to present a rationale for such an opinion.
Should a member proceed to provide a letter related to a vaccination exemption, members should clearly indicate that it is for psychological reasons and that, in keeping with Principle 10.3 of the Standards, “ must render only those professional opinions that are based on current, reliable, adequate, and appropriate information.” As well, it is important that members recognize they could be held accountable should an employer or other party mistakenly accept their letter as a valid official “medical exemption”, and remember that making a record, or issuing or sign a certificate, report or similar document that they know or ought to know is false misleading or otherwise improper, is an act of professional misconduct.
Originally published in HeadLines Volume 1 Issue 2
Regulated Health Professionals are subject to Directive #2 of the Chief Medical Officer of Health. This directive states that: In the gradual restart of services, Health Care Providers must comply with the requirements as set out in “COVID-19 Operational Requirements: Health Sector Restart” (May 26, 2020 or as current), including, but not limited to, the hierarchy of hazard controls.
The hierarchy sets out the following measures, in order of priority:
- Elimination and Substitution – examples include not having patients physically come into the office/clinic, use of telemedicine, etc;
- Engineering and Systems Control Measures – examples include physical barriers like plexiglass partitions;
- Administrative Control Measures – examples include active screening, passive screening (signage), and visitor policies;
- Personal Protective Equipment – examples of PPE include gloves, gowns, facial protection (including surgical/procedure masks and N95 respirators), and/or eye protection (including safety glasses, face shields, goggles, or masks with visor attachments).
As noted previously, the Ministry recommendations must be general enough to apply to all health care providers. As a result, some of the examples provided may not be applicable to psychological services.
The Ministry is clear that PPE controls, such as masks, are the last tier in the hierarchy of hazard controls. Accordingly, they should not be relied on as a stand-alone primary prevention program. The Operational Requirements clearly state: Given community spread of COVID-19 within Ontario and evidence that transmission may occur from those who have few or no symptoms, masking (surgical/procedure mask) for the full duration of shifts for HCPs and other staff working in direct patient care areas is recommended.
Some local areas have enacted by-laws requiring mask use in indoor public settings, with exceptions to this requirement for health care providers. It is likely that such exceptions have been made in order to enable some health care procedures which cannot be performed while a mask is being worn.
The College continues to recommend that services should be provided virtually when possible. When in-person services are required, members should wear masks and require clients to do so in enclosed spaces, unless this is clinically contraindicated.
Originally published in HeadLines Volume 1 Issue 2
This can be a difficult situation to navigate and we are advising members to make best efforts to negotiate resolution of such problems.
The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 require:
2.1 General Conduct
A member must conduct himself/herself so that his/her activities and/or those conducted under his/her direction comply with those statutes and regulations that apply to the provision of psychological services.
and,
3.1.2 Employment Settings
A member must assume responsibility for the planning, delivery, and supervision of all psychological services he/she provides to a client. Members working as employees must make best efforts to ensure that their work setting adheres to the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 in the planning, delivery, supervision and billing practices of all psychological services provided.
The College is not authorized to regulate workplaces, only the conduct of individual members. As stated above, members are required to make best efforts to ensure that the work setting adheres to the Standards. This may involve escalating the issue within their organization and seeking outside assistance where necessary. Hopefully, in most cases, collaborative communication will help to resolve any “standoffs”.
Members may wish to advise those with the authority to grant their requests that Directive #2 has been issued to all Regulated Health Providers under Section 77.7 of the Health Protection and Promotion Act, 1990 and requires Health Care Providers to consider which services should continue to be provided remotely and which services can safely resume in-person with appropriate hazard controls and sufficient PPE.
Originally published in HeadLines Volume 1 Issue 2
The COVID-19 Operational Requirements: Health Sector Restart indicates that health care professionals should perform active screening, although we understand this can be assigned to a staff person. Screening should be done with the client. If it is believed that a client is unable to answer the screening questions reliably, it should be done in discussion with a person’s parent or caregiver.
The Operational Requirements state: Patients should be screened over the phone for symptoms of COVID-19 before coming for their appointments. If possible, any visitor accompanying a patient to an appointment, should also be screened prior to the appointment. The latest COVID-19 Patient Screening Guidance Document on the MOH COVID-19 website should be used and may be adapted as needed and appropriate for screening purposes. If a patient screens positive over the phone, the appointment should be deferred if possible and the individual referred for testing.
Originally published in HeadLines Volume 1 Issue 2
The College’s expertise and role is limited to professional regulation. It is beyond the purview of the College to provide clinical guidance to members. The College trusts that members practicing the profession have the knowledge, skill and judgment required to make appropriate clinical decisions.
With the large number of tools, techniques and tests in use, members should obtain current guidance from the test publishers about the administration procedures and the applicability of norm-based scores. At those inevitable times when answers are not clear, members may find it helpful to discuss these issues with other clinicians who they believe have relevant expertise.
As in all cases, interpretation of test results includes consideration of the context in which an assessment is conducted. The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 which guide members in making such judgments include:
10.1 Familiarity with Tests and Techniques
Members must be familiar with the standardization, norms, reliability, and validity of any tests and techniques used and with the proper use and application of these tests and techniques.
Practical Application: At times, a member may provide services in what would be considered an emerging area of practice. In such situations, a member should inform clients that the services being offered may not, yet, have been subjected to extensive research and validation. As with any informed consent process regarding the provision of services, clients would be informed of the risks, benefits and alternatives available.
10.2 Familiarity with Interventions
Members must be familiar with the evidence for the relevance and utility of the interventions used and with the proper use and application of these interventions.
10.3 Rendering Opinions
A member must render only those professional opinions that are based on current, reliable, adequate, and appropriate information.
10.4 Identification of Limits of Certainty
A member must identify limits to the certainty with which diagnoses, opinions, or predictions can be made about individuals or groups.
We have become aware from members that test publishers are providing guidance about how measures which rely on standardized administration procedures may be utilized. It is a member’s responsibility to ensure that they are using the tools properly, based on empirical evidence and good clinical judgment.
Originally published in HeadLines Volume 1 Issue 2
If someone has tested positive, the local Public Health agencies are expected to follow appropriate protocols with respect to notifying those who must be notified.
There does not appear to be a requirement for a member of the College to make a mandatory report of someone who has identified themselves as, or is suspected of being, COVID-19 positive. There are, however, provisions in the Health Protection and Promotion Act, 1990 that authorize the Chief Medical Officer of Health to make an Order requiring the release of confidential information, as specified in that Order. If ordered to provide information, the College would not expect a member to put themself in contempt of the Order. To date, we have not heard about any members receiving such Orders. If one is unsure of the nature of such an Order or the information it may require by released, one should seek legal advice.
If concerned about individuals who may have crossed paths with an infected person, it would be permissible and reasonable for a member to provide general de-identified information to other clients and suggest they may wish to be tested. One should, however, take care not to provide any information that could identify the other person.
Confidentiality provisions under the Personal Health Information Protection Act, 2004 (PHIPA) prohibit the disclosure of personal health information without authorization by the client, other than in specified circumstances. Exceptions to the duty of confidentiality are set out in sections 39 (regarding certain health programs) and 40 (regarding risk of serious bodily harm). It is important to remain aware that these exceptions permit one to make disclosure but do not require this. When one uses the discretion to make a disclosure without a client’s permission, only that information which is necessary for the purpose of eliminating or reducing a significant risk of serious bodily harm to a person or group of persons should be disclosed. Additionally, such information should only be disclosed to a person who is in the position to eliminate or reduce the risk.
If unsure about whether a disclosure is permissible, it may be useful to obtain the opinion of a qualified legal professional. Many professional liability insurance policies entitle the policy holder to pro-bono legal advice.
CPD - Program Requirements
Unless you hold a Certificate of Registration with “Retired” status, you are expected to maintain professional competence, in anticipation of your return to practice. There is a great deal of flexibility in terms of how you may earn CPD credits. While many of the opportunities to earn Category A (Professional Activities) credits involve active professional practice, there are opportunities for credit to be earned that are not directly related to professional practice.
Please note that it is possible to satisfy the requirements of the program by earning as few as 10 credits over two years from Category A. Category B (Continuing Education) credits can be earned outside of the context of active service delivery. If you are experiencing circumstances that make it impossible to satisfy the requirements of the program, please contact the College to discuss this.
CPD - Program Administration
While it is expected that you will be continuously engaged in professional development activities, you are only required to declare that you have completed the requirements of the mandatory CPD program at the end of each two-year CPD cycle. Bearing this in mind, you must begin to record credits you earn at the beginning of each cycle. Ordinarily, the cycle will begin on July 1 and end on June 30th, two years later.
Please note: only for members beginning the first cycle in 2017, credits may be collected for the period between May 8th, 2017, and June 30, 2019.
Members with a Certificate authorizing Autonomous Practice or an Inactive Certificate must complete the Self-Assessment Guide (SAG) every two years. Those with a Certificate Authorizing Supervised Practice or Interim Autonomous Practice must complete the SAG every year, however, the CPD cycle is still two years in length, so the CPD declaration must be made every second year. If your current registration number ends in an even number you must begin and end your CPD cycle in years ending in an even number. If your current registration number ends in an odd number you must do so in years ending in an odd number.
The following table indicates when to begin formally recording CPD credits and when your first CPD Declaration of Completion will be due.
| Certificate class and Registration Number at the time a Declaration is required: | Credits earned beginning on the following dates may be counted towards completion of the requirements: | First CPD Declaration Required |
| Supervised Practice “odd” | July 1, 2017* | June 30, 2019 |
| Interim Autonomous Practice “odd” | July 1, 2017* | June 30, 2019 |
| Autonomous Practice “odd” | July 1, 2017* | June 30, 2019 |
| Academic “odd” | July 1, 2017* | June 30, 2019 |
| Inactive “odd” | July 1, 2017* | June 30, 2019 |
| Supervised Practice “even” | July 1, 2018 | June 30, 2020 |
| Interim Autonomous Practice “even” | July 1, 2018 | June 30, 2020 |
| Autonomous Practice “even” | July 1, 2018 | June 30, 2020 |
| Academic “even” | July 1, 2018 | June 30, 2020 |
| Inactive “even” | July 1, 2018 | June 30, 2020 |
*Credits earned from May 2017 will be accepted for this transitional cycle only.
If you have been acquiring CPD credits for two years, regardless of changes to your Certificate of Registration, those credits would apply. In other words, despite any changes in your Certificate of Registration, you will have completed the requirements of the program if you earn 50 credits in the two years leading up to the declaration date. If you receive notice that a declaration is due but have not had a full two years in which to earn the 50 credits, the College will provide you with an alternate declaration that recognizes this.
The Quality Assurance Committee will conduct random audits of member participation in the CPD Program. When audited, members will be required to provide the Quality Assurance Committee with a detailed list of their CPD activities, as well as supporting documentation of their activities, wherever these are available. It is recognized that formal documentation of participation is not available for some activities such as case conferences, self-learning or group viewing of webinars in which individual registration is not required. In such circumstances, formal documentation is not available and members will not be expected to provide it.
Yes. If you are selected for a Peer Assisted Review, the reviewer will request access to your record and documentation of your CPD activities.
CPD - Activities Eligible for Credit
The intention of the program is to ensure that within a two year period, members are engaged in at least the minimum amount of required professional development. For that reason, only activity within the two years prior to a declaration of completion may be counted.
The categories are comprehensive and it is expected that every CPD activity can be included within one of the categories provided in the program description and tracking sheet available from the College. Examples provided of the activities within each of the categories convey the range of activities members may count. It should be noted that these lists are examples and are not intended to be all-inclusive. Members are expected to use their own judgment in deciding whether the particular activities they choose meet their professional development needs, as identified in the Self-Assessment Guide, and which particular requirements of the CPD program each activity will satisfy.
A peer can be a professional in the field of psychology or a person who is qualified as a professional in a field relevant to the practice of psychology. Interdisciplinary interaction is encouraged by the College.
Professionally relevant programs/workshops are those events that enhance knowledge relevant to the psychological services a member provides. Content need not be primarily psychological in nature but must be directly related to the services provided by the member. For example, a member working within the correctional system might benefit from an educational event provided by correctional officers regarding the management of offenders within the prison system.
If you have earned “CE” credits by attending live events like conferences and conventions you may claim credit for attendance at the conference or convention under Category A and also for the specific time you spend within the presentations as CE credits in Category B. For example, if attending a convention from 9 a.m. until 4 p.m., you would earn one credit for spending the day with peers under Category A8 and, if attending presentations for 4 hours, an additional 4 credits under Category B for the 4 hours you were engaged in learning during the presentations
The College doesn’t accredit or approve courses. Members must determine whether an activity is suitable for CPD credit. If the activity is relevant to one’s CPD, it is eligible for credit. Similarly, the College also doesn’t approve or endorse specific CE accreditation bodies. Members are expected to use their own judgment in determining the appropriateness of specific CE crediting organizations.
Any activities relevant to your Ontario practice are eligible for credit, wherever they take place.
Yes.
Examples of how to satisfy this requirement include participating in any professional activity or continuing education activity related to ethical issues, including those addressing local jurisdictional issues. The following are a few examples of the many ways you may earn these credits:
-
Attending an event run by a local professional group or participating in an organized discussion group that addresses professional ethics
-
Working with a workplace ethics committee
-
Attending the Barbara Wand Symposiums, in person or by webinar, or watching the archived recordings
-
Completing online continuing educational programs offered by professional associations
-
Participating in a College or professional association activity related to ethical practice
-
Attending, or watching webcasts of public lectures which are offered by universities and other educational organizations that are relevant to professional ethics
-
Reading books and articles that are relevant to professional ethics
Teaching psychology requires ongoing research, up-to-date knowledge, and an ongoing exchange of information between teachers and students. For this reason, it is regarded as valuable CPD.
Formally monitoring progress towards specific outcome goals, either for individual clients or on an organizational level, can be a useful mechanism for determining whether an approach to practice is effective or not and is a valuable learning experience. Active participation in either activity is eligible for CPD credit.
It is recognized that Conducting Formal Research is a distinct activity and that not all of those involved in conducting research are responsible for writing about it. Additional credit may be obtained for writing, reviewing, and editing in Category A4.
The CPD program is intended to ensure that you maintain competence within your existing authorized areas of practice and with your authorized client populations. The development of competence in additional areas of practice or with additional populations must be undertaken through a much more comprehensive and rigorous process, beyond what would ordinarily be required to satisfy the CPD requirements. If you are seeking to expand your areas of authorized practice or authorized client populations, please contact the College.
If participating in your own therapy leads you to gain knowledge, experience, and/or skills that advance your ability to provide professional psychological services it may be counted as one type of activity under category A1 for a maximum of ten credits every two years.
Peer Review under category A1 (Professional Consultation/ Interaction) is meant to include peer review of another member’s practice. Reviewing another member’s professional reports could be counted under category A1 as it is a form of professional consultation. Reviewing articles for publication may be counted under category A4 (Writing, Reviewing, Editing).
CPD - Categorization of Activities
The College will require you to provide a declaration that you have satisfied all of the requirements of the program at the end of each two-year CPD cycle. You will not be required to provide details describing your CPD activities, or supporting documentation unless the College specifically asks you to do so.
This may occur when:
- You have not submitted your Declaration of Completion of the CPD requirements by the College’s deadline
- You have been selected when the Quality Assurance Committee conducts a random audit of member participation in the CPD program
- You are subject to an Assessment or Review under the College’s Quality Assurance Program, including a Peer and Practice Assessment
Category A (Professional Activities) includes activity-based experiences believed to enhance professional development by developing competencies in the multifaceted areas related to one’s practice. In addition to keeping abreast of scientific knowledge, members are encouraged to include other components of service enhancement in their CPD activities. Examples of these include but are not limited to, reviewing evidence for the purpose of evidence-based decision making, keeping up to date with technology, and enhancing interpersonal and multicultural competence.
A maximum of 10 credits for any one type of activity may be counted in section A1. If what you do in the peer consultation group is different than what you would do in the individual consultations, then you could consider it to be two different activities and you could acquire 20 credits in all. There will be judgment calls to be made when deciding ‘what belongs where’ and we are leaving it up to members’ own good judgment to make these decisions, so long as they can provide a reasonable rationale for the decision if asked for one. Incidentally, you can earn peer consultation credits for consulting with any professionals, not only psychologists and psychological associates, if the discussion is with a professional and the issues are relevant to your practice.
Credit for general attendance at events in Category A8 is meant to reflect the value, in and of itself, inherent in interacting with colleagues and participating in the social, interpersonal, professional, and scientific activities which are part of the milieu of conferences and conventions. It is believed that being among peers enhances professional development as this leads to awareness of the practices of colleagues and of the ideas, problems, and challenges that are present in the professional environment. Continuing Education credits available under Category B reflect the acquisition of information from attending presentations while at the event. This applies whether the events are attended in person or via technology.
No, the 10 credits related to ethics are not additional credits. You must ensure that a minimum of 10 of the credits earned in satisfaction of the 50 credits required in total are related to professional ethics.
CPD - Documenting Activities
Many conferences and workshops provide participants with a certificate of attendance and this would be sufficient verification. For organized events that do not provide such certification, a record of your registration or payment will suffice. For other activities where formal documentation is not provided, like case rounds, self-guided learning, time spent conducting research or observing a webinar with a group where individual sign-up is not required, you may simply state that you have participated in the activity and provide a description of the activity including the organization, group, people, publication and/or other resources involved. Here is a sample completed CPD tracking form which provides the level of detail suggested.
The College will not require you to pay for an “official CE credit” document. Your statement, program information from the provider indicating that formal CE credits are available and confirmation of registration will be sufficient.
No. The electronic tracking tool has been developed as an aid for members who wish to use it. So long as you maintain an accessible record of your CPD activities, you may keep track of them in any manner you wish.
You must retain your records for at least five years after completion of your last CPD cycle.
Peer Assisted Review
The Peer Assisted Review (PAR) process has been in place since the fall of 1999. Each year, a number of members are randomly selected to have their practices reviewed as part of the College’s Quality Assurance Program. The PAR is described below in a series of FAQ’s, in an effort to provide members with an understanding of the process.
Any member with a Certificate of Registration for Autonomous Practice is a potential participant in the PAR process.
Any member who has not completed the mandatory Self-Assessment requirement of the College is required to participate in a PAR. Additionally, members are identified for participation using a computerized random, or stratified random, selection process.
Two members of the College; an assessor appointed by the Committee and a reviewer nominated by the member being reviewed.
Generally, both the assessor and the reviewer will have knowledge of the member’s area(s) of practice, population(s) served and practice setting(s).
The member undergoing a review will have an opportunity to indicate whether they believe that there is any reason a potential assessor should not conduct the review.
Efforts are also made to select an assessor who has either undergone a review themselves or who has previously acted as an assessor or reviewer.
The reviewer is nominated by the member being reviewed and can be a colleague or associate. They may act as a support to the member. While this individual is nominated by the member being reviewed, in accepting this role the reviewer understands and agrees to act as an agent of the College and therefore to act in the public interest.
The assessor and reviewer must undertake and agree to:
- Participate in the College’s Peer Assisted Review Assessor and Reviewer training before conducting the review, if I have not already done so within one year prior to the date of the review
- Maintain confidentiality, as required by s.36 of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991, S.O. 1991, c. 18
- Familiarize themselves with the Legislation, Regulations and the Standards of Professional Conduct relevant to the practice they will be reviewing
and attest that:
- They have held a certificate of Registration for Autonomous Practice with the College of Psychologists of Ontario for at least five years
- They are currently in active practice as a psychologist or psychological associate
- They are free of any conflict of interest or bias, or any appearance of either, with respect to the review
- Neither themselves, nor the individual they will be reviewing is in a position of power with respect to the other
The review is conducted at the member’s practice setting. In cases where a member works in more than one setting, the appropriate location for the review will be determined in discussion with the member.
Members normally set aside a morning or afternoon for the review as it can take from three to four hours.
The scheduling is determined by the assessor and reviewer, in consultation with the member being reviewed. It is expected that every effort will be made to schedule the review at a mutually agreeable, and convenient time for all participants and which takes into account the least disruption to the member’s work schedule.
The assessor and reviewer will together observe the member’s place of practice, interview the member using a structured interview form and review some of the member’s clinical records.
The Reviewers will provide a report to the Quality Assurance Committee. The Committee appointed assessor must provide a copy of the report as well as notice of the right to make submissions to the Quality Assurance Committee within 14 days of receipt of the report, directly to the individual who has been reviewed.
The Quality Assurance Committee will review the Report and any submissions the member has made and determine whether any action is required, in the public interest.
One of three outcomes is possible from the review:
- Meets Standards without any qualification: This is a relatively frequent outcome in which no areas for improvement are identified. Some suggestions may be offered by the reviewers that the member may find helpful to incorporate into his/her practice.
- Would meet Standards with minor modifications: This is a relatively frequent occurrence in which minor areas for improvement are identified which the member has agreed, with the reviewers, to address within a specified time frame. The Quality Assurance Committee will confirm with the member and the reviewers that the recommended and agreed upon changes have been completed.
- Is Significantly Below Acceptable Standards: While this is not a frequent occurrence, when major areas for improvement are identified, the Quality Assurance Committee will address these directly with the member.
If you have any questions regarding the PAR please contact the Quality Assurance Coordinator at qualityassurance@cpo.on.ca
Professional Corporations
The word “ancillary” is not defined in the Business Corporations Act, 1990 from which this condition arises. It’s the College’s position that, in this context, it means subordinate, subsidiary, or secondary to the practice of psychology. Despite similarities in the practices, Social Workers, Social Service Workers and Registered Psychotherapists are practicing distinct other professions.
Psychology may only be practiced in Ontario by members of the College of Psychologists or those supervised by them. Professional services provided by autonomous practitioners of different professions would not be considered the practice of psychology. It’s the College’s understanding that the practice of other professions would not be considered to be ancillary to the practice of psychology.
While both are corporations, the rules that stipulate their ownership structures and the activities that they can undertake are different.
Professional Corporations
The shareholders of professional corporations must all be members of the same health regulatory college as must all the officers and directors of the professional corporation. Further, the only business that a professional corporation is permitted to undertake is the practice of the profession and activities that are related to or ancillary to the practice of the profession. Every professional corporation is also required to obtain a Certificate of Authorization from the college of its members before it is permitted to conduct its business.
Practice Management Corporations
In contrast, the ownership rules of corporations that manage practices are more relaxed. Members of different health professions, non-health professionals and even family members can be shareholders as well as officers or directors. Corporations that manage practices are not permitted to practice any regulated health profession and the shareholders of these corporations are not permitted to practice their regulated health profession through the corporation. This does not mean that members cannot work for non-professional corporations owned by others. Rather, it means that when they are working for a such a corporation, they are practicing as individual health professionals outside of the corporation. Because these corporations are not permitted to practice a regulated health profession, they are not required to register with the College or Colleges of their shareholders.
The College is not in a position to legal advice with respect to the Business Corporations Act. Your legal and business advisors can provide specific advice relevant to your circumstance.
There are differences between professional corporations and those that manage practices and are not professional corporations. A corporation that manages a practice, and is not a health professional corporation, is not permitted to practice a regulated health profession and hence is not required to register with the College or Colleges of their shareholders.
The College is not in a position to legal advice with respect to the Business Corporations Act. Your legal and business advisors can provide specific advice relevant to your circumstance.
This is a business decision. The College recommends that you discuss your plans with an accountant or lawyer who specializes in this area.
No, if you are practising the profession of psychology through a corporation it may only be a psychology professional corporation that operates under a Certificate of Authorization issued by the College of Psychologists of Ontario.
Members who wish to practise through a corporation are required to obtain a Certificate of Authorization from the College. Detailed information and application forms can be found on the College Website.
You may submit the application and supporting documents via email to corporations@cpo.on.ca
Or by regular mail to:
110 Eglinton Avenue West
Suite 500
Toronto, Ontario M4R 1A3
Please contact corporations@cpo.on.ca to have a to have an invoice posted to your account to submit the application fee.
Once a complete application package has been received by the College, it takes 2 to 3 weeks for processing. The effective date of the certificate is the date the complete package and application fee was received.
The application fee for a new Certificate of Authorization is $350.
There are restrictions on the names of professional corporations. Please refer to the College Guide to an Application for Certificate of Authorization for Professional Corporation. Briefly, the names of professional corporations must:
- Include the surname of one or more shareholders of the corporation as the surname is set out in the College register;
- Indicate the health profession practised by the shareholders (i.e. “psychology”);
- Include the words “Professional Corporation” or “Société professionnelle”.
For detailed information, please refer to section 3.2 of the Business Corporation Act, 1990 and Ontario Regulation 39/02 under the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991. It is also wise to consult with the College before setting up your corporation to ensure that the name is appropriate.
Examples: Smith Psychology Professional Corporation; Smith and Jones Psychology Professional Corporation; John Smith Psychology Professional Corporation; J. Smith Psychology Professional Corporation.
You may use a different practice name than the name of your professional corporation. You must list every practice name under which the professional corporation practices when completing the application form.
Speak to your own lawyer or accountant about the requirements for registering business names.
The College does not approve or comment on practice names, and there are no specific rules for practice names other than to ensure the name does not violate the section of the Advertising Regulation, (see section 18.1) This section prohibits in advertising, and so also in naming, something that would suggest uniqueness, specialty or something that is false or misleading.
Only members of the College of Psychologists of Ontario.
Yes, if all the shareholders, officers and directors of the holding company are registered members with the College of Psychologists of Ontario.
No. Members intending to incorporate must do so under the Ontario Business Corporations Act. For forms and instructions on how to incorporate, contact the Companies Branch of the Ministry of Government Services website or call 416-314-8880.
Health profession corporations incorporated in a jurisdiction outside Ontario, including corporations federally incorporated under the Canada Business Corporations Act, cannot obtain a Certificate of Authorization from the College. They must incorporate under the Ontario Business Corporations Act, and satisfy the conditions and requirements of the RHPA to be considered a health profession corporation in Ontario.
The certificate is valid for one year and must be renewed annually on the date of authorization. Members will be emailed a renewal package approximately 6 weeks prior to this date.
The fee for renewal of a Certificate of Authorization is $250.
The requirements related to issuance and renewals of Certificates of Authorization are set out in the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 (RHPA) and the Certificates of Authorization Regulation. They apply equally to all regulated health professions in Ontario. The general requirement for annual renewal is written into these regulations as a fixed component. The College asks members to complete only what is required under the RHPA.
A Corporation Profile Report is a document issued by the Ontario Ministry of Public and Business Service Delivery (formerly the Ministry of Government and Consumer Services) that indicates that the corporation is registered and active. The legislation sets out the requirements for the annual renewal of your Certificate of Authorization. One of those requirements is that a current-dated Corporation Profile Report accompanies your annual renewal application regardless of how long your health professional corporation has been in existence.
You may obtain a newly issued Corporation Profile Report by:
-
- Contacting the Ministry of Public and Business Service Delivery (formerly the Ministry of Government and Consumer Services) directly:
375 University Avenue, 2nd Floor, Toronto, M5G 2M2 | Tel: 416-314-8880 or 1-800-361-3223 https://www.ontario.ca/page/ontario-business-registry - Using any online website that provide the service to generate the report
- Contacting the Ministry of Public and Business Service Delivery (formerly the Ministry of Government and Consumer Services) directly:
The Corporation Profile Report does not need to be certified.
You must submit articles of amendment filed with the Ministry of Government Services if you made any changes, such as a name change, to the corporation since incorporation or the last renewal.
Yes – In fact, the College must revoke a professional corporation’s Certificate of Authorization in a number of circumstances. These include:
- The corporation ceases to be eligible to hold a Certificate of Authorization.
- The corporation ceases to practise the profession in respect of which the Certificate of Authorization was issued.
- The corporation fails to comply with one or more of the requirements for a renewal of the Certificate of Authorization.
- The corporation carries on any business that is not the practice of the profession governed by the College or activities related to or ancillary to the practice of that profession.
If the College revoked a Certificate of Authorization, the professional corporation must apply for a new one and meet the eligibility requirements in effect at the time of the new application. At that time one must submit the required application and supporting documents and pay the application fee.
Professional Practice
Originally published in Volume 2 Issue 1 of HeadLines.
In the practices of most members, the answer to this question can be found in the Health Care Consent Act, 1996 (HCCA) and the Personal Health Information Privacy Act, 2004 (PHIPA).
One must first establish whether the child has the capacity to make their own independent decisions in these situations. The HCCA and the PHIPA do not specify chronological ages of consent but instead set out the test for determining whether any individual, including a child, is capable of making their own health care decisions. The determination of capacity must be made by the Health Care Provider or the Health Information Custodian, as the case may be. The analogous tests for capacity to be applied are set out in section 4 of the HCCA and section 21 of PHIPA, respectively.
If the child is not believed to be capable, a substitute decision-maker for the purpose of the HCCA is generally deemed to play the same role with respect to PHIPA.
Section 20 of the HCCA and Section 26 of PHIPA provide specific advice with respect to the hierarchy of potential decision-makers when a child is not believed to be capable of making their own decisions. It also sets out the mechanisms for deciding what must happen when a person with the right to make decisions is not available or willing to assume decision-making responsibility. The legislation also addresses what to do if there is conflict between two individuals having equal ranking in the hierarchy.
Generally, a parent can give or refuse consent on behalf of an incapable child unless this authority has been lawfully granted to a children’s aid society or other person. If both parents do not have the same rights under an Agreement or Order, a parent with custodial rights prevails over a parent who has only a right of access. In situations where the statute does not spell out clearly which parent is entitled to make the decision, statutory interpretation is necessary. Given the high stakes for all individuals involved, the most prudent course of action is to obtain independent legal advice.
The College’s August 2005 Bulletin provides additional guidance with respect to this issue.
Originally published in Volume 2 Issue 1 of HeadLines.
The answer to this question depends upon various decisions made by the organization, including who is the Health Information Custodian (HIC), a term which is used and defined in the Personal Health Information Protection Act, 2004 . For the purposes of answering this question, either a health care practitioner or a person who operates a group practice of health care practitioners may be a HIC. There may only be one HIC and it should be the person who will have ultimate responsibility for the collection, use, disclosure, security, and retention of the information. .
The HIC must ensure that their identity is made clear to all concerned, including the client. A client must provide informed consent for a specified individual or organization to collect information about them.
A Health Information Custodian may have an “agent”. This is defined in PHIPA as a person that, with the authorization of the custodian, acts for or on behalf of the custodian. The HIC may, for example, appoint the service provider working in the HIC’s organization to be their agent.
Copies of information may be shared with those with a need to have the information in their possession but may only be provided to anyone other than the HIC or agent with client consent. The number of copies of the same information is directly correlated to the risk of loss or unauthorized access to the information. The fewer number of copies there are of a document, the lower the risk of loss or unauthorized disclosure.
There is no prohibition against storing information in more than one file/location. Standard 9.1 of the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 requires that a member must make best efforts to ensure that the member’s records are complete and accessible; this applies whether the record is kept in a single file or in several files and whether the record is housed in one location or at several locations. It is suggested that when records are not maintained in one file or location that a note is placed in each location indicating the location(s) of any other information.
The provision of psychological services is regulated locally within most North American provinces, states and territories, for the purpose of protecting those located within the province, state, or territory.
In most jurisdictions, including Ontario, services are deemed to be delivered in the location of the client. Each jurisdiction has its own statutes and regulations and has the authority to take action with respect to unauthorized practice. For this reason, permission must be sought from the College or Board in the same province, state or territory as the person who will be receiving services is physically located.
Members may provide services to an individual located in another jurisdiction, but only if they have been authorized by the College or Board in that jurisdiction to do so. From time to time, requirements of other jurisdictions can change and members are encouraged to check with the jurisdiction in which the client is located. If the psychology regulator in the other jurisdiction permits one to practice in their jurisdiction, it would also be important to confirm that one’s professional liability insurance coverage extends to one’s work with an individual in the other jurisdiction.
Members may be interested to know that there is a Memorandum of Understanding with Nunavut. At this point in time, there are no such agreements with other provincial regulators.
The College of Psychologists of Ontario does not have the authority to grant permission to provide psychological services anywhere other than in Ontario. College members may provide services in other jurisdictions wherever they are permitted to by the psychology regulatory body in that jurisdiction, so long as they do so in accordance with the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017.
Ontario statute requires that one must be a member of the College of Psychologists of Ontario, or supervised by a member of the College, to provide psychological services to a person located in Ontario.
The Psychology Act, 1991 states:
Restricted titles
8 (1) No person other than a member shall use the title “psychologist” or “psychological associate”, a variation or abbreviation or an equivalent in another language.
Representations of qualification, etc.
(2) No person other than a member shall hold himself or herself out as a person who is qualified to practise in Ontario as a psychologist or psychological associate or in a specialty of psychology.
Idem
(3) A person who is not a member contravenes subsection (2) if he or she uses the word “psychology” or “psychological”, an abbreviation or an equivalent in another language in any title or designation or in any description of services offered or provided.
Exception for university faculty
(4) Subsections (1) and (3) do not apply to a person in the course of his or her employment by a university.
Temporary, limited membership is available to individuals licensed to provide psychological services in other jurisdictions allowing them to provide services for a period of up to 12 months. To learn more and to apply for this form of membership please click here.
In order to provide psychological services to an individual located in Ontario, or hold out as qualified to do so, the Psychology Act, 1991 requires that one must be a member of the College of Psychologists of Ontario, or be working under the supervision of a member of the College. There may be circumstances in which there is a need to include, by way of videoconferencing or teleconferencing, an individual located in Ontario in a session conducted with your clients in your own home jurisdiction. So long as the involvement of the person in Ontario is limited to their role as a resource in treating or assessing the clients in your own local jurisdiction, and not for the purpose of treating or assessing the individuals located in Ontario, they may be included. In such a case, they may be considered a collateral resource for the benefit of the clients receiving your service in your own jurisdiction.
Please be advised that provisions made for service provided during the pandemic are no longer available as of May 15, 2023. If you have a question about providing psychological services to an existing client who is temporarily in Ontario, please review the College’s information regarding temporary and time limited registration found here
The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 state that:
11.1 Fees and Billing Arrangements
Members must reach an agreement with an individual, group or organization concerning the psychological services to be provided, the fees to be charged and the billing arrangements prior to providing psychological services. Any changes in the services to be provided must be agreed to by the client before service is delivered or fees are changed. Fees must be based on amount of time spent and complexity of the services
rendered.
Practical Application: Fees for services should be determined on a consistent basis, regardless of the payer. A member may, however, offer pro bono services or apply a sliding scale to ensure access to services and affordability.
While this Standard is most often thought of in the context of initiating services with a new client, it also can be read to apply with respect to the ongoing provision of services. That is, “providing psychological services” could be read to mean each instance of providing a psychological service. It would be inappropriate for a client to learn that their fees had been increased when they receive a bill for a service that had already occurred. Increased fees may be an important consideration for clients in the ongoing informed consent to service process and some clients may need to reconsider whether they are able, or prepared, to continue at the new proposed rate.
There is no specific period of notice for a fee change set out in any Regulations or in the Standards as this is a matter of professional judgment. Adequate notice of the change however, is important and there may be clients who experience a fee increase as akin to indirect termination of therapy.
In cases where the client may not agree to an increased fee, and a member is not prepared to continue to provide services at the existing rate, guidance regarding the termination of services can be found in section 8 of O.Reg. 80.1/93: Professional Misconduct. This section of the Regulation states that termination of service that is needed is an act of professional misconduct unless:
i. the client requests the discontinuation,
ii. the client withdraws from the service,
iii. reasonable efforts are made to arrange alternative services,
iv. the client is given a reasonable opportunity to arrange alternative services, or
v. continuing to provide the services would place the member at serious personal risk.
Although there are informal ‘rules of thumb’ with respect to ‘winding down of therapy’, often based upon the length of time a person has been receiving treatment, the College does not set any particulars in this regard. If the client requires additional services but can not or will not pay the increased rate, it would be reasonable and appropriate to work with them for a time period that, in the member’s professional judgment, is sufficient to arrange for a transfer of care to another service provider and avoid any harm due to a disruption of treatment.
This can be the case with respect to such factors as age, language, race, culture, or gender diversity and is a legitimate concern. In the absence of appropriate norms, one would need to use clinical judgment to interpret the client’s response to items and, in accordance with the following Standards:
A member must render only those professional opinions that are based on current, reliable, adequate, and appropriate information.
The answer to this question depends upon who has been identified as the Health Information Custodian. Under the Personal Health Information Protection Act, 2004 (PHIPA), it is possible that either a health care practitioner or a person who operates a group practice of health care practitioners can act as the Health Information Custodian (HIC). While either is possible, only one must be established at the onset of services. Generally, this will be the particular individual or entity they authorize to collect their Personal Health Information.
If, in this scenario, the operator of a group practice is not the HIC, then, the following Standard is applicable:
4.1 Responsibility of Supervisors of Psychological Service Providers
If members are supervising psychological services provided by a member holding a certificate for supervised practice or any other unregulated or regulated service provider who is not an autonomous practice member of the College, the clients are considered to be clients of the supervisor…
It then follows that the records are considered to be the records of the supervising member. This is supported by the following additional Standard:
9.1.2 Members Responsible for Supervising Supervised Practice Members and Non- Members
Members supervising Supervised Practice members and non-members are responsible for the security, accessibility, maintenance, and retention of records.
If the organization is not the HIC, at the end of the engagement, in most case it is the supervising member who is the HIC and the records must remain with them for the required retention period.
A member must identify limits to the certainty with which diagnoses, opinions, or predictions can be made about individuals or groups.
An American Psychological Association article about assessing people who are transgender provides one example of how to conduct an assessment where no appropriate norms have been identified. In the absence of specific guidance concerning an identified group, registrants are advised to document their approach to interpreting test responses. This can be helpful in the event that assessment results are challenged and, of at least as much importance, the exercise of writing out a rationale can help make the activity as objective as possible.
In order to answer this question, it is important to consider what is meant by “consulting” as it can be understood to mean different things in different contexts. Consultation is defined in the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 as:
the provision of information, within a relationship of professionals of relatively equal status, generally based upon a limited amount of information that offers a point of view that is not binding with respect to the subsequent professional behaviour of the recipient of the information.
If this describes the nature of the relationship with the agency, then the organization is generally considered to be the client. In the case of an organizational client, the member providing consultation is required to maintain records in accordance with the following Standard:
9.3 Organizational Client Records
1. Members must keep a record related to the services provided to each organizational client.
2. The record must include the following:
a) the name and contact information of the organizational client;
b) the name(s) and title(s) of the person(s) who can release confidential information about the
organizational client;
c)the date and nature of each material service provided to the organizational client;
d) a copy of all agreements and correspondence with the organizational client; and
e) a copy of each report that is prepared for the organizational client.
The “nature of each material service provided to the organizational client” in c) above, should likely include sufficient information to address queries about the quality of the particular consultation, should that information ever be needed.
An organizational client record must be retained for at least ten years following the organizational client’s last contact. If the organizational client has been receiving service for more than ten years, information contained in a record that is more than ten years old may be destroyed, if the information is not relevant to services currently being provided.
It is the responsibility of the individual providing services to ensure that proper client consent is obtain for the service being providing. A person acting as a consultant to a service provider would not likely be in a position to seek consent from the person receiving services from the consultee. The consultant may, in fact, never come into contact with the person receiving services from the consultee. In some cases they may not even know their name.
If a member is identified as a “consultant” but they are personally providing the psychological assessment, diagnosis, opinion or intervention, as opposed to “consulting” to or supervising another service provider, this would likely be considered a direct service. In this case, all of the Standards relevant to direct service provision, including those pertaining to consent and record-keeping, would be applicable.
In circumstances where it is unclear whether one is providing direct service or consultation, it may be useful to ask: Is this a service I would provide autonomously to an individual or family in a clinical practice, or is it providing advice to another autonomous service provider who is simply looking for the input with respect to clinical decisions they must make themselves?
Most of the queries we have received related to this problem have been asked in the context of an individual who is transgender, where a client may be capable of making their own decisions may not be in a position to effect a legal name change, due to age or an institutional or family situation. Ideally, such issues should be discussed as part of the informed consent process, as early as possible and preferably before beginning the assessment. If the client agrees to have both their legal and preferred names in the report, that would avoid any confusion to readers of the report with respect to who the report is about. If the client does not provide permission to note both names and there is a need to include the client’s non-preferred name, or to indicate that the name used in the report is not the same as the client’s legal name, this will require careful navigation, in order to protect the client’s dignity and to avoid making a potential misrepresentation. In such a case, it would be prudent to obtain independent legal advice before proceeding.
When addressing issues related to a trans person’s identify, the Ontario Human Rights Commission provides the following guidance:
- Preventing discrimination because gender identity and gender expression – 9 reasonable bona fide requirements
2. Preventing discrimination because gender identity and gender expression – 7 forms of discrimination
3. Preventing discrimination because of gender identity and gender expression – preventing and responding to discrimination
This article, by the APA provides some guidance for how to determine when treating two ‘related’ individuals could become problematic.
In summary, the decision about whether or not to take on individual clients who are related either through family, friendship or are involved with each other in any other way will depend on a critical evaluation of the circumstances, nature of that relationship and the potential for cross involvement at any time.
We recognize that ‘word of mouth’ is often how clients find their therapists, so it is likely that many members have clients who know each other. Each situation will likely present different risks and degrees of risk. When separately treating individuals who are friends with each other, there is a possibility that one client may want to discuss the other client for a variety of possible reasons. This could be problematic if the information they want to share is related to the issues you are treating the other person for and that information may be relevant to your formulation of the other case, regardless of whether or not it is verifiable information. In other words, this could be seen as a problem with respect to protection of both confidentiality and objectivity. Working with clients who you know to be friends with each other should be avoided whenever possible due to the complications that can arise. and increase the possibility that you may contravene the following Standards of Professional Conduct:
8.1 Collection, Use and Disclosure
Members are responsible for ensuring that consent is obtained with respect to the collection, use and disclosure of personal information and personal health information in a manner required by legislation applicable to the relevant service.
10.5 Freedom from Bias
Members must provide professional opinions that are clear, fair and unbiased and must make best efforts to avoid the appearance of bias.
13.1 Compromised Objectivity, Competence or Effectiveness Due to Relational Factors
Members must not undertake or continue to provide psychological services with an individual client when their objectivity, competence or effectiveness is, or could reasonably be expected to be, impaired. This could be due to the members present or previous familial, social, sexual, emotional, financial, supervisory, political, administrative, or legal relationship with the client or a relevant person associated with the client. This prohibition does not apply if the services are delivered to an organizational client and the nature of the professional relationship is neither therapeutic nor vulnerable to exploitation.
This article, published by the American Psychological Association provides an example of the difficulties which could arise when treating two ‘related’ individuals could become problematic.
A decision about whether to take on individual clients who are related either through family, friendship or are involved with each other in any other way will depend on a critical evaluation of the circumstances, nature of that relationship and the potential for cross involvement at any time. While treating individuals who are associated with each other is not strictly prohibited, if the community is large enough, it would be better to find another practitioner who would not be in such a potentially challenging situation.
As you likely know, dual relationships are not strictly prohibited but should be avoided, unless the client is unable to find another competent and available service provider.
Before agreeing to provide the service, you may wish to think about whether your previous professional relationship could lead to any concerns that this assessment was anything less than highly objective. While you are likely to work hard to remain objective, this can be difficult if you do hope for a particular outcome for a client you have supported through their struggles. Even if you can be perfectly objective, if your findings were to be challenged, it could be alleged that you weren’t, due to your previous alliance with the client.
It would also be important to consider whether there is any possibility that the client may seek intervention from you in the future, and whether your role as an assessor might prevent them from doing so. This could be the case if they were unhappy with the outcome of the assessment and this prevented them from returning to therapy with you, causing them to have to “start all over again” with another therapist.
Although multiple relationships are not strictly prohibited, the College has observed that members trying to be helpful by having multiple different service relationships with the same clients have inadvertently entered into challenging situations.
While the College Standards set out the minimum length of time for record retention, there are no rules against keeping information indefinitely. It is not advisable though, to keep information which is not likely to be useful any longer than one needs to, due to the risks associated with unauthorized access to any record.
It’s our understanding that many members do keep a log of the files they have destroyed, with information such as you have outlined in your question. It is important to know that the information in such a record is considered Personal Health Information and that these lists themselves are subject to the same privacy legislation and Standards as the records themselves were, because they identity individuals who have received health care. If you do decide to keep such a record you might also consider including the date of destruction
Following the successful completion of an Oral Examination, and after you are issued a Certificate of Registration authorizing Autonomous Practice, you will no longer require supervision in your authorized areas of practice and client populations. Although formal supervision is no longer required, consultation and other forms of peer support can be of great value throughout your professional career.
Under Supervised Practice, your supervisor was responsible for your adherence to the Legislation, Regulations, Standards and Ethical Guidelines applicable to your practice. If you have been issued a Certificate of Registration authorizing Autonomous Practice you are now fully accountable for the discharge of your own professional and ethical responsibilities.
While the applicability of various statutory and ethical obligations can be straightforward when taking on new clients, taking on the management of professional responsibilities with clients who were initially seen under supervision often leads to questions about such matters as informed consent, fees and billing, and clinical records.
Continuing to Work with Clients you had Previously been Supervised with
If you will be continuing to work with individuals who you worked with during your period of Supervised Practice, it is important consider the changes your new Autonomous Practice registration entails. It’s important to:
- Ensure that clients who wish to continue working with you as an autonomous practitioner, know that you will now be solely responsible now for their care, that your supervisor no longer considers them to be their clients and that you are no longer under supervision;
- Engage in an independent informed consent process with clients, outlining your new, autonomous professional responsibilities and confirm agreement with respect to what services you will be providing, and on the fees you will be charging;
- Clarify that the personal health information collected during your period of Supervised Practice must remain with the person or organization who was the Health Information Custodian during your supervision;
- If you are to be considered the Health Information Custodian going forward, you may obtain a copy of records made to date only with the client’s consent; information about who is the Health Information Custodian can be found here: Who “Owns” the Clinical Record? In a group practice comprised of members authorized for autonomous practice, who can access, contribute to, and hold copies of the clinical record?
A member of the College of Psychologists of Ontario may provide services to clients located in Ontario, whether or not the College member is in Ontario at the time. In other words, a member of the College of Psychologists of Ontario who is travelling outside of the province may provide services via technology to clients located in Ontario while they are away. Specific information about the provision of services via technology may be found in in Standard 15 of the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017.
First, it is good to know that you are helping them to address these issues, as a colleague. It does not appear that you have a duty to report this situation.
There are two situations in which you may have a mandatory reporting obligation, but this does not sound like it is one of them. The two situations are set out in Section 85.2 and Section 85.5 of the Health Professions Procedural Code, being Schedule 2 of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991. The first applies to operators of facilities in which a health professional provides services:
Reporting by facilities
85.2 (1) A person who operates a facility where one or more members practise shall file a report in accordance with section 85.3 if the person has reasonable grounds to believe that a member who practises at the facility is incompetent, incapacitated, or has sexually abused a patient.
From your description of the situation, it doesn’t sound like you operate a facility in which this colleague practices, therefore this section would not apply.
The second relevant section of the Code applies to reporting by employers, etc.
Reporting by employers, etc.
85.5 (1) A person who terminates the employment or revokes, suspends or imposes restrictions on the privileges of a member or who dissolves a partnership, a health profession corporation or association with a member for reasons of professional misconduct, incompetence or incapacity shall file with the Registrar within thirty days after the termination, revocation, suspension, imposition or dissolution a written report setting out the reasons.
Same
(2) Where a member resigns, or voluntarily relinquishes or restricts his or her privileges or practice, and the circumstances set out in paragraph 1 or 2 apply, a person referred to in subsection (3) shall act in accordance with those paragraphs:
- Where a person referred to in subsection (3) has reasonable grounds to believe that the resignation, relinquishment or restriction, as the case may be, is related to the member’s professional misconduct, incompetence or incapacity, the person shall file with the Registrar within 30 days after the resignation, relinquishment or restriction a written report setting out the grounds upon which the person’s belief is based.
- Where the resignation, relinquishment or restriction, as the case may be, takes place during the course of, or as a result of, an investigation conducted by or on behalf of a person referred to in subsection (3) into allegations related to professional misconduct, incompetence or incapacity on the part of the member, the person referred to in subsection (3) shall file with the Registrar within 30 days after the resignation, relinquishment or restriction a written report setting out the nature of the allegations being investigated. 2014, c. 14, Sched. 2, s. 12.
Application
(3) This section applies to every person, other than a patient, who employs or offers privileges to a member or associates in partnership or otherwise with a member for the purpose of offering health services. 1993, c. 37, s. 23.
Once again it does not appear that you would have a reporting obligation unless you are the colleague’s employer and due to concerns of incapacity you terminated their employment or revoked, suspended or imposed restrictions on their privileges to practice or you dissolved a partnership, a health profession corporation or association with them.
Hopefully, with your collegial support, this individual will be able to mitigate the risks to themself and their clients and find relief from their distress. If it appears advisable for your colleague to obtain professional services, then you should consider referring them to an appropriate mental health professional, to avoid becoming involved in a dual relationship.
This is a situation that requires some definitional framing, before looking at the issue of feedback.
The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 define a “client” as:
an entity receiving psychological services, regardless of who has arranged or paid for those services. A client can be a person, couple, family or other group of individuals with respect to whom the services are provided. A person who is a “client” is synonymous with a “patient” with respect to the administration of the Regulated Health Professions Act (1991).
This means that the person who has been assessed is, from the perspective of the College, the client. Members are expected to be proactive in ensuring that clients are aware of their rights, including the right to access information about themselves, in accordance with the following Standard:
3.2 Clarification of Confidentiality and Professional Responsibility to Individual Clients and to Organizations
In situations in which more than one party has an interest in the psychological services rendered to a client or clients, members must, to the extent possible, clarify to all parties, prior to rendering the services, the dimensions of confidentiality and professional responsibility that must pertain in the rendering of services. The provision of psychological services on behalf of an organizational client does not diminish the obligations and professional responsibilities to individual clients.
Practical Application: The need for clarification may arise, for example, in the provision of an assessment of a claimant in an insurance matter, where the insurer has retained the assessor. Regardless of the wishes of the insurer, members are under all of the obligations that pertain to a client within these Standards and the relevant privacy legislation. This includes providing access to the individual or their authorized representative to their personal information and any reports or records which members have in their possession unless prohibited by law or they are otherwise permitted to refuse access.
The requirement to provide feedback, upon request by the client, is addressed in Ontario Regulation 801/93 Professional Misconduct:
The following are acts of Professional Misconduct:
…
13. Failing to provide a truthful, understandable and appropriate explanation of the nature of an assessment, intervention, or other service following a client’s request for an explanation.
…
21. Failing, without reasonable cause, to provide a report or certificate relating to a service performed by the member, within a reasonable time, to the client or his or her authorized representative after a client or his or her authorized representative has requested such a report or certificate.
Similarly, members are required to make information, including assessment results, available to all clients and authorized representatives, under the following Standard:
8.2 Access by Client or Client’s Authorized Representative
Members are responsible for ensuring that access to an individuals’ personal or personal health information is provided to the individual and/or their authorized representative unless prohibited by law or the member is otherwise permitted to refuse access.
While it may at first seem possible to find a technical “out” to providing feedback to someone who has not actually requested it, the Personal Health Information Protection Act, 2004 (PHIPA) specifies that consent to disclose information must be obtained from the person who has been assessed (or an authorized Substitute Decision Maker), and only if they have knowledge of the purposes of the disclosure. The consent must also be related to the information to be disclosed. In other words, there is a positive responsibility on the part of the Health Information Custodian to ensure that the client has been provided with an opportunity to make a free and informed decision about the disclosure of the information that would be disclosed.
There are two situations in which members have a duty to report incapacity-related concerns. These are set out are set out in Section 85.2 and Section 85.5 of the Health Professions Procedural Code, being Schedule 2 of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991. Neither of these appear to apply to a situation in which the concern regarding incapacity is with a client.
If you believe that this individual is putting members of the public at risk you can always make a report to the professional’s College, with their consent. In addition, Section 40 of The Personal Health Information Protection Act, 2004 also permits you to make a voluntary report, without the client’s consent, if you believe, on reasonable grounds that such a disclosure is necessary as they are putting clients at significant risk of serious bodily harm:
Disclosures related to risks
- (1) A health information custodian may disclose personal health information about an individual if the custodian believes on reasonable grounds that the disclosure is necessary for the purpose of eliminating or reducing a significant risk of serious bodily harm to a person or group of persons.
Section 13, specifically 13.2, of the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 requires members to responsibly assess their well-being and avoid impairment:
- Professional Objectivity
13.2 Compromised Objectivity, Competence or Effectiveness Due to Other Factors
A member must not undertake or continue to provide psychological services when personal, scientific, professional, legal, and financial or other interests could reasonably be expected to:
- a) impair his/her objectivity, competence or effectiveness in delivering psychological services; or
- b) expose the client to harm or exploitation.
Members are expected to use their professional judgement in considering their personal workload tolerance. The Quality Assurance Committee had developed a Self-Care Plan to provides some guidance in this area. The Quality Assurance Program requires that every member formally reflect upon their own need for self-care and mitigate the risk of harm to their own well-being and consequently that of their clients.
The College has not identified “parents” as a specific population to whom one needs particular authorization to consult to or otherwise work. The answer to your question then is: It depends upon the specific focus of the consultation.
If the parenting work involves psychoeducation, that is, providing parents with information about child development and advice about how they can address childhood difficulties, then it would make sense that a practitioner has been deemed to have the requisite knowledge, training, and experience required to understand the developmental factors at play with children/adolescents being ‘parented’. In this situation, authorization to work with children and adolescents would be expected.
If the focus of the work is to help parents improve their relationship with their child, then specialized knowledge, skill, and experience in the area of family dynamics is important. For this reason, authorization to work with families would be necessary.
Similarly, if the focus of the work is helping the parents work together as a couple, then authorization to work with couples, would be appropriate. Likewise, if the work involves assisting an individual parent who for personal reasons experiences challenges in interacting with a child and this requires them to receive individual therapy to address their own difficulties, authorization to work with individuals within that parent’s own age group would be required. Since you are authorized to work with adults, assuming that the parents are adults, then this would not be problematic.
Basically, one size can’t fit all, and the system of authorized populations allows for flexibility because of all of the possibilities with this kind of work.
Section 125 of the Child, Youth and Family Services Act, 2017 (CYFSA) sets out the duty to report a child in need of protection. It states:
125 (1) Despite the provisions of any other Act, if a person, including a person who performs professional or official duties with respect to children, has reasonable grounds to suspect one of the following, the person shall immediately report the suspicion and the information on which it is based to a society. Society is defined in the legislation as an agency designated as a children’s aid society under subsection 34 (1);
In considering this section of the legislation, there are two components to contemplate. First, there is nothing in the legislation which suggests that the suspected abuse or neglect must have occurred in Ontario to be reportable. Therefore, one is obligated to make a report regardless of where the suspected concerning behaviour occurred.
Second, the duty to report is to a “society” which the Act states is an agency designated by the Minister of Children and Youth Services as a children’s aid society. Since the Minister only has the authority to designate an agency as a “society” within Ontario, the obligation to report “to a society” must be to an appropriate agency within Ontario.
This analysis suggests that if a member has an obligation to report a suspicion of abuse or neglect which occurred outside of Ontario, they would have a duty to report to an Ontario CAS. It would then be up that agency to determine the best course of action to take but the member would have fulfilled their legislative obligation.
Section 125 also sets out the nature of emotional harm that a child must be experiencing, or which it is reasonably expected would experience, to necessitate a report, if the harm results from, or would be expected to result from the actions, failure to act or pattern of neglect on the part of the child’s parent or the person having charge of the child.
A: The Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario (IPC) recently addressed this issue in PHIPA DECISION 133, October 2020.
The Decision sets out the statutory limits to what one may charge, as follows:
[12] Under PHIPA, custodians have the discretion to charge a fee for providing an individual with access to their own personal health information. Sections 54 (10) and (11) state:
Fee for access
54 (10) A health information custodian that makes a record of personal health information or a part of it available to an individual under this Part or provides a copy of it to an individual under clause (1) (a) may charge the individual a fee for that purpose if the custodian first gives the individual an estimate of the fee.
Amount of fee
(11) The amount of the fee shall not exceed the prescribed amount or the amount of reasonable cost recovery, if no amount is prescribed.
The legislation does not prescribe an amount for “reasonable cost recovery”. In providing Reasons in Decision 33, the Adjudicator for the IPC states, previous IPC orders and PHIPA Decision 17 conclude that the 2006 fee scheme set out in the proposed regulation to PHIPA provides the best framework for determining the amount of “reasonable cost recovery” under section 54(11) of PHIPA.
| 2006 Fee Scheme | |
| Flat rate including: – 15 minutes of review – 20 pages of photocopies – packing and mailing the records – administrative tasks |
$30.00 |
| Photocopies or computer printouts after the first 20 pages | $0.25 per page |
| Review of the records after the first 15 minutes | $45 for every 15 minutes of review by a health information custodian after the first 15 minutes. |
The Decision provides a detailed analysis of the particular case and anyone facing this sort of issue is advised to read the entire Decision. For ease of reference, here is an excerpt from the Reasons that the Adjudicator gave for a finding that the health professional’s charges were excessive:
[44] In PHIPA Decision 111, I determined that not every type of record containing personal health information subject to PHIPA requires the same amount of time for review. … records with standard, predictable content require only a straightforward review with minimal time needed to determine whether they contain information to which access may be refused. For these types of records, I determined a review time of five seconds per page was appropriate. I found that other records, which by their nature, have the potential to contain information to which access may be refused, require a more detailed and lengthy review. For these types of records, I determined a review time of two minutes per page was appropriate… I have no evidence before me to suggest that any of the records at issue have the potential to contain personal health information that may required a more detailed and lengthy review…
[46] As a result, and in the absence of evidence to the contrary, in my view it is reasonable to conclude that the 27 pages of responsive records would require only a straightforward review at five seconds per page. Accordingly, I find that a reasonable amount of time for the custodian to review 27 pages of records containing the complainant’s own personal health information is encompassed in the first 15 minutes of review that are accounted for in the set fee of $30 per request. Given the nature and number of responsive records, I find that when the 2006 fee framework is applied, the custodian is not permitted to charge review fees in excess of what is accounted for in the set fee of $30. I accept that, in the circumstances, this amounts to “reasonable cost recovery” as required by section 54(11) of PHIPA.
While this reasoning is not enshrined in legislation or in formal guidelines, the precedent set by this, and previous Decisions should be considered by members when they set fees for the copying of records.
Although there are no specific requirements identified with respect to formal notetaking in a consultation relationship, there are specific requirements with respect to services to Organizational Clients. The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 define an Organizational Client as: an organization, such as a business, community or government that receives services that are directed primarily at the organization, rather than to the individuals associated with that organization.
If the social worker is thought of as operating a business, it is the business (as opposed to the social worker’s clients) to whom you are providing consultation. This would mean the records are Organizational Client Records. The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 set out the following requirements for Organizational Client records as follows:
9.3 Organizational Client Records
- Members must keep a record related to the services provided to each organizational client.
- The record must include the following:
- the name and contact information of the organizational client;
- the name(s) and title(s) of the person(s) who can release confidential information about the organizational client;
- the date and nature of each material service provided to the organizational client;
- a copy of all agreements and correspondence with the organizational client; and
- a copy of each report that is prepared for the organizational client.
Although the “nature of each material service provided” is not described, it can be reasonably understood that this means information about the issues discussed and advice given should be recorded. This would apply to any consultation, including those involving members of other professions.
The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 require that supervising members must be authorized to autonomously provide services to the specific populations before supervising others in that work. Furthermore, the Standards also requires that
Supervising members must assess the knowledge, skills and competence of their supervisee and provide supervision as appropriate to the supervisee’s knowledge, skills, and competence, based on this assessment;
Unless a supervisor has sufficient information about a client and the client’s difficulties, they would not be able to provide adequate supervision appropriate to the supervisee’s knowledge, skills and competence.
It is the responsibility of a supervisor to be sufficiently familiar with the client’s demographics and needs before permitting their supervisee to commit to provide services. The adequacy of the supervision could be in question if a supervisor reviews and signs off on reports without having been involved in a direct or supervised intake process, or does not actively supervise the work leading up to any final reports.
Even though the Standards do not require supervisors to meet and interact with clients receiving services under their supervision, a supervisor should only permit a supervisee to work with a client after they have satisfied themselves that the client is within their authorized areas of practice and belongs to a population with whom they are authorized to work.
The Definition of Practice Areas are published as part of the Registration Guidelines. Within the Guidelines, the definition of Counselling Psychology stresses fostering and improving human functioning by helping individuals solve problems, make decisions and cope with stresses of everyday life. These can include work/career/education, family and social relationships, and mental health and physical health concerns. In other words, these are the types of difficulties which may cause distress to an otherwise well-functioning or psychologically healthy individual. Some common examples of such problems are bereavement, unemployment, marital separation, or bankruptcy, etc. Generally, an individual presenting as having a disorder of behaviour, emotion or thought, should be assessed and treated by a member authorized in Clinical Psychology.
As described in the Definition of Practice Areas, members who practice Counselling Psychology, at a minimum, are expected to have “the ability to formulate and communicate a differential diagnosis in order to develop an appropriate counselling intervention and to identify clients who must be referred elsewhere”.
In contrast to that of Counselling Psychology, the definition of Clinical Psychology, as described in the Definition of Practice Areas, is “the application of knowledge about human behaviour to the assessment, diagnosis and/or treatment of individuals with disorders of behaviour, emotions and thought”.
It is sometimes unclear at the initial stages of involvement whether a client has a “disorder”, and this is an important reason that those authorized in Counselling Psychology be able to perform a differential diagnosis. When a client presents with indicators of a disorder of behaviour, emotion or thought, a member who is not authorized in Clinical Psychology should refer them to a member authorized in this area.
If, at the time of referral, an individual presents with indicators that suggest they may have a diagnosable disorder, it would be most appropriate for an assessment to be conducted by someone qualified to work with those with clinical disorders. One should carefully consider the implications of beginning to work with someone that is likely to need to be transferred to someone else’s care. This could be quite disruptive to the client and the clinical relationship, and may even be damaging to their well-being and/or treatment.
At times, the extent of a client’s difficulties may not be apparent at the initiation of services, and it may later become evident that the client is suffering from a clinical disorder. If a member, authorized in Clinical Psychology, is not available to accept a referral, it would be permissible to obtain supervision from someone so authorized. This should be considered a “last resort” however, and not a “workaround” for appropriate authorization.
It is appropriate for private practitioners, including contractors, to be compensated based on time spent and the complexity of services provided. If providing additional incentives to treatment providers could be reasonably expected to lead to decisions about service planning that are motivated by factors beyond client needs this could be problematic. For example, this could be problematic if compensation rather than client needs lead to practicing the profession while in a conflict of interest and/or providing services which are not likely to benefit the client; both of which are considered acts of Professional Misconduct. Members are advised to support their staff and contractors in ensuring that client need is the primary consideration in service planning.
As required by Standard 4 of the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017, members supervising anyone who is not a member of the College and any member with a Certificate of Registration Authorizing Supervised Practice must co-sign all psychological reports and formal correspondence related to psychological services prepared by their supervisee.
The term “formal” has not been officially defined so members must use their professional judgment based upon the particular circumstances of each situation.
In generally, formal documents would likely include printed or electronic communications which ordinarily require the person responsible for the information to provide their endorsement of the information in the form of a signature. This might include letters, reports, official memos, and emails about a client which would reasonably be expected to provide information about a client to anyone outside of the organization in which the supervision is occurring.
When in doubt about whether to co-sign a document, it may help to consider that a supervisor’s signature is meant to provide an assurance to readers of the information it has been endorsed by the professional responsible the service. Even if not strictly required to co-sign a document, supervising members may do so if they wish to inform readers that they endorse the contents.
We’ve heard about this incorrect position from enough people to assume that, at some time in the past, it must have been promulgated widely. While the legislation permits one to refuse access to personal health information in some limited circumstances, including raw data from psychological tests, it does not prohibit one from allowing access to it. In many cases, it is expected that raw data will be provided, even with non-members.
A list of exceptions to the right of access to personal health information can be found in section 52 of the Personal Health Information Protection Act (PHIPA), 2004. Most of the exceptions relate to the expectation of serious risk associated with the disclosure.
Members who have insufficient cause to withhold raw data may have concerns about the risk of releasing the information to those who are not sufficiently trained to interpret it. In such cases, members are advised to attach a statement to the raw data indicating that raw data from standardized tests can lead to incorrect conclusions, and that this information should only be interpreted by those who are regulated psychological service providers with adequate training and experience in the interpretation of test results.
Detailed further information about the release of raw data can be found on the College’s Professional Practice FAQ pages.
It is a client’s right to decide who their personal health information may be shared with, subject to some exceptions set out in the Personal Health Information Protection Act (PHIPA), 2004. The Office of the Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario has published some helpful information about the Circle of Care, a colloquial term describing how one may rely on implied consent and the Lock Box, the colloquial language used to describe how a client may limit what can be shared where one could ordinarily have relied upon implied consent. All members who have not yet reviewed these documents, should familiarize themselves with these concepts and rules.
While there may be an argument that a member is not technically violating PHIPA if they provide information based upon implied consent, it isn’t really in the spirit of the legislation to do so, particularly if one believes a client who understood their rights, might capably choose to limit disclosure of their personal health information.
If there is reason to believe that a client would not want their personal health information shared, even if they have not sought to have the information ‘placed in a lock box’, one should consider the impact of sharing the information on the therapeutic alliance or on the client’s trust of other health care professionals, if the client believes their privacy has not been respected.
The answer to this question depends upon the reason for involving family members in the treatment of an individual.
Individual therapists appropriately may involve a client’s family member(s) for the purpose of facilitating support for intervention with the individual. For example, a person’s family member(s) might be asked to become involved in making changes in the client’s environment to facilitate change or to be trained to provide reinforcement for desirable behaviours as part of a behavioural intervention program. A family member could also be asked to attend sessions with a person who, for some reason, may not be able to successfully participate in individual therapy without support. In such a scenario, the family member(s) attending would not be the object of the intervention themselves but would instead be there to help the client obtain optimal benefit from the individual therapy.
If the purpose of involving family members is to facilitate any changes in the family dynamics or the way in which family members interact with one another, this would be viewed as an family intervention. For example, this would be the case when it is the therapist’s intention to address an individual’s symptoms or behaviours of concern by addressing the patterns of interaction between family members which precipitate or maintain the difficulties. In order to provide such intervention to families, one must have specialized knowledge and training and the specific authorization of the College.
This question has been answered by the Office of the Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario and can be found in the Frequently Asked Questions; Personal Health Information Protection Act September 2015, on page 31 of the document.
The answer reads as follows:
Yes. PHIPA permits the disclosure of personal health information without consent, if permitted or required by another law. For example, this means that PHIPA does not interfere with the Workplace Safety and Insurance Act (Act), where that Act requires a hospital or health facility, which provides health careto a worker claiming benefits under the insurance plan, to give the WSIB such information relating to the worker as the WSIB may require. This requirement also applies to a health care practitioner who provides health care to a worker or is consulted with respect to a worker’s health care. When requested to do so by an injured worker or the employer, the Act requires a health care practitioner treating the worker to give the WSIB, the worker and the employer prescribed information concerning the worker’s functional abilities.
The Standards of Professional Conduct directly address the use of technology in the generation of assessments, reports and statements:
10.7 Use of Computer-Generated Reports
Information obtained from computer-generated assessments, reports or statements must not be substituted for a members professional opinion.
Members are free to responsibly use technological advances as an adjunct to their own assessments and interventions, however, it is the position of the College that these professional activities must always be actively mediated by members who are authorized to provide the services and that members must remain fully accountable for services provided in their names.
To date, there is insufficient scientific evidence to demonstrate the effectiveness and safety of using ChatGPT or other Artificial Intelligence (AI) to assess or treat mental health conditions and the risk to clients may outweigh any potential benefits. Anyone considering the use of AI to assist or augment their services should ensure, as part of the informed consent process that clients understand how technology is being used to assist them, what the risks are of technological error, and also what risks there are to their privacy when personal information is being used in an AI context.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 1 of HeadLines.
In Ontario, there is no duty to warn, if one interprets “duty” to mean a mandatory requirement. That is, there is no obligation to report concerns that a client/patient may pose a danger to themselves or others. It is important to understand however, that this does not mean that one cannot, or should not, take some action in the face of such serious concerns. The Personal Health Information Protection Act, 2004 (PHIPA) sets out a member’s obligations with respect to maintaining the confidentiality and privacy of personal health information. The legislation does provide an exception to the duty of confidentiality where a member finds it necessary to notify someone of a serious risk to a person’s safety. PHIPA states:
40 (1) A health information custodian may disclose personal health information about an individual if the custodian believes on reasonable grounds that the disclosure is necessary for the purpose of eliminating or reducing a significant risk of serious bodily harm to a person or group of persons. 2004, c. 3, Sched. A, s. 40 (1).
A key concept within this section of PHIPA is contained in the words “may disclose”. PHIPA does not oblige a member to make such disclosures, but it permits one to do so “for the purpose of eliminating or reducing a significant risk of serious bodily harm”. With this purpose in mind, PHIPA reinforces a member’s need to use their knowledge of the client/patient and their professional judgement to determine the best, most appropriate, action to take.
With the relaxation of pandemic-related restrictions on in-person services, some members are exploring whether to return to in-person service delivery or to continue providing all services virtually. There is no specific prohibition against offering online services.
Members must use their professional judgment in deciding whether to offer in-person vs. virtual services, taking into consideration the needs of each individual seeking services and the available evidence regarding efficacy.
Members are expected to provide services in a safe and effective manner. If a member wishes to restrict their practice to virtual services, they must decide which populations and problem areas can be effectively assisted without in-person contact, and under what circumstances this would be appropriate.
There is no ‘one size fits all’ when it comes to planning service delivery in psychology. It may be that some clients are more comfortable with on-line services and might be more likely to engage in services provided via technology and some intervention models may lend themselves to on-line delivery more than others. Members should also consider some concerns that have been raised about services delivered via technology. These include:
• loss of many visual cues and other sensory inputs which are less accessible via the computer screen or telephone than when physically present with a client;
• increased risk to breaches of confidentiality;
• increased need for vigilance concerning professional boundaries and personal privacy; and
• issues of equity, as some clients will not have access to technology, sufficient familiarity and/or competence in using it, and/or the necessary adequate privacy.
Members providing virtual care must adhere to all of the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 including, but not limited to, Standard 15, Use of Technology in the Provision of Psychological Services. An additional resource members may find useful is the American Psychological Association’s Guidelines for the Practice of Telepsychology. This is a helpful guide in reflecting upon the delivery of services via technology. Some of the areas addressed in the article are the need to: regularly monitor and assess the progress of the client/patient to determine if the continued provision of telepsychology services remains appropriate and beneficial; discuss any concerns with the client/patient; and appropriately terminate remote services and provide assistance in arranging alternative services, if necessary.
If a member initially agreed to provide in-person services to a client; transitioned to on-line services during the pandemic; and wishes to continue with on-line services beyond the point at which it seems necessary, this can be problematic if the client wishes to return to in-person services. In such a situation, a member may decide to terminate services against a client’s wishes, but should be mindful of the section 1.8 of O. Reg. 801/93: Professional Misconduct Regulation which sets out the manner in which one can do so that would not be considered professional misconduct.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 1 of HeadLines
The legislation does not direct a member to contact any particular organization, institution or individual should it be determined there is a need to take some action. In considering a breach of confidentiality under section 40 of PHIPA, it is important that, in keeping with the stated purpose, the disclosure be made to someone who is in a position to ‘eliminate or reduce a significant risk of serious bodily harm’.
When faced with serious concern about a client’s/patient’s risk of harm to self or others, members have to make the difficult judgment about who to contact in this time of crisis. When initially reviewing the limits of confidentiality regarding risk of harm with a client/patient, members may wish to discuss this with the client/patient. That is, engage the client in a discussion of who they believe should be called in the event of a crisis. The client/patient may identify a family member, other health care provider, close friend, member of the clergy, a community worker, an organization with which they have been involved or some other individual. While the ultimate decision rests with each member based on their best clinical judgement, taking into account their understanding of the client/patient and the particular situation, this previous discussion may prove helpful in deciding upon the most appropriate action.
It is important to make a distinction between situations of client/patient risk of harm to themselves or others, often referred to as “duty to warn” and other mandatory reporting obligations. Section 40 of PHIPA does not apply to situations where one has reasonable grounds to suspect that a child is in need of protection or one suspects abuse or neglect in a retirement or long-term care facility. In these situations, mandatory reporting to the appropriate authority is required.
The answer to this question requires interpretation of legislation and College staff are not qualified or authorized to provide legal advice. Members who are considering refusal of a specific request for information may wish to obtain independent legal advice, given that release of confidential information, or the refusal to do so, can be a high-stakes decision for all concerned. The following information may be of assistance in obtaining legal consultation.
The Personal Health Information Protection Act, 2004 (PHIPA) sets out the applicable rules to be considered when addressing a request for personal health
information.
Personal Health Information is defined, in section 4.(1)(a) of the Act, as information that “relates to the physical or mental health of the individual, including information that consists of the health history of the individual’s family. . .”
Section 1 (b) of PHIPA states that one of the purposes of the Act is “to provide individuals with a right of access to personal health information about themselves, subject to limited and specific exceptions set out in this Act”. The Act also provides that information an individual is entitled to access can be provided to another party, with the consent of the individual or of the individual’s authorized substitute decision-maker.
Whenever faced with a decision about whether to provide access to information contained in a client record, it is a good idea to review the list of exceptions to the requirement to do so. These exceptions are set out in in Section 52(e) of the Act where one is not required to allow access to information if,
(e) granting the access could reasonably be expected to,
i. result in a risk of serious harm to the treatment or recovery of the individual or a risk of serious bodily harm to the individual or another person,
ii. lead to the identification of a person who was required by law to provide information in the record to the custodian, or
iii. lead to the identification of a person who provided information in the record to the custodian explicitly or implicitly in confidence if the custodian considers it
appropriate in the circumstances that the identity of the person be kept confidential;
The Act, section 52(2) goes on to say that a health information custodian may provide only parts of a person’s record “that can reasonably be severed from the part of
the record to which the individual does not have a right of access”. When a decision is made to sever part of a file before releasing the record, section 54 of the Act provides
specific guidance about how to do this.
The Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario recently considered a complaint about an agency’s refusal to grant one family member access to the entirety of a family’s therapy records. In PHIPA Decision 158, the Commissioner found that the Personal Health Information (PHI) of each family therapy participant is theirs alone and not PHI of the other therapy participants. They went on to say that family therapy records may contain “communal” or “shared” information that can form part of each participant’s PHI. Communal or shared information was described as information about family health history, overall family relationships or dynamics, as well as general themes that arose in the course of family therapy.
The Commissioner ultimately decided that the complainant’s right of access under PHIPA was limited to only to PHI that can reasonably be severed from the records. The Decision explains that the Act is intended to enable individuals to access information about their family health history allowing them to make informed decisions about their own health care but that anything beyond shared or communal information, may have been collected with an expectation that it would remain confidential.
The Decision further explained that this best respects the confidentiality of that information; fosters trust between family therapy participants and custodians; promotes participant autonomy over access to their own personal health information; and promotes candid discussion and unguarded participation in family therapy sessions.
The Decision indicated that the right of access to information is limited by section 52(3), of the Act, which provides that an individual will only have a right of access to an entire record if the record is “dedicated primarily” to their personal health information. The following examples of factors to consider in determining whether a record is “dedicated primarily” to the personal health information of a requester are provided:
- the quantity of personal health information of the requester in the record;
- whether there is personal health information of individuals other than the requester in the record;
- the purpose of the personal health information in the record;
- the reason for creation of the record;
- whether the personal health information of the requester is central to the purpose for which the record exists; and
- whether the record would exist “but for” the personal health information of the requester in it.
The following “best practices” are suggested within the Decision:
- At the outset of therapy, establish ground rules for what can be discussed, what information will be recorded, and who will have access to the records;
- Document this understanding in the health record;
- Identify documents (including chart notes) that relate to one participant and those that relate to all participants; and
- When considering requests to access family or group therapy records, refer to documented informed consent and other records to identify participants’
expectations, and categorize records as communal or relating to one or more participants before granting access to any records.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 2 of HeadLines
The College doesn’t specify hard borders between age ranges for the different population groups but recognizes that there are not always clear demarcations with respect to population groups, particularly with respect to age. Members are expected to use their professional judgment to determine whether, in all the circumstances, the person’s status is consistent with the status of those for whom they are authorized to provide service. For example, when trying to determine whether a client, at a border age, is an “adult”, “adolescent”, or for that matter a “senior”, it would be important to consider whether the person’s abilities, life circumstances and challenges are consistent with those which would normally be expected within the population groups for which the member is authorized to work.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 2 of HeadLines
As members know, the College has defined Authorized Areas of Practice. The definitions for the authorized areas of practice focus on the nature of difficulties the services are intended to address, as opposed to the specific type of service offered. In order to answer questions like this it may be most helpful to keep this distinction in mind.
The Practical Application posted with Standard of Professional Conduct, 2017 5.1 states: In deciding whether one is authorized and competent to provide a service, the nature of the client’s presenting difficulties will generally determine whether the member has the appropriate and required authorization. For example, if a client who has suffered a traumatic brain injury has been referred because of a need to assess the nature of their neuropsychological deficits, it is expected that the member providing the assessment would have clinical neuropsychology as an authorized area of practice. If the person was referred because of difficulty performing activities of daily living or occupational requirements, it is expected that the member would be authorized to work in the area of rehabilitation psychology. If the person was referred because of suspected anxiety or depression, then it is expected that the member would be authorized to practice in clinical psychology…
It’s likely that most of what are often called “psychoeducational assessments” are meant to help identify the reason an individual has difficulty learning in an educational environment and to provide information for the purpose of planning for remediation of these difficulties. If there is reason to believe that the nature of difficulties is neuropsychological in nature, then it would appear reasonable for someone with authorization in the area of Clinical Neuropsychology to assess the client.
At the same time, authorization in School Psychology requires certain knowledge not generally required for the practice of Clinical Neuropsychology, including knowledge of:
- academic, instructional and remedial techniques;
- interdisciplinary team approach for case management, program planning and crisis intervention;
- consulting, counselling, and primary, secondary and tertiary intervention programs and techniques;
- systems and group behaviours within, and related to, the school organization, including school climate and culture.
If making specific recommendations which require such knowledge, it’s expected that a member who has not acquired this knowledge would seek the professional guidance of another member who is authorized to practice School Psychology.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 2 of HeadLines
Members may provide services to an individual located in another jurisdiction, but only if they have been authorized by the College or Board in that jurisdiction to do so. If the psychology regulator in the other jurisdiction permits this practice, it would also be important to confirm that one’s professional liability insurance coverage extends to one’s work with an individual in the other jurisdiction.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 3 of HeadLines
The Professional Misconduct Regulation and Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 do not specifically address the issue of whose name to put on an invoice. Therefore, one must ensure adherence to the broader rules when deciding about how to proceed regarding what information to put on an invoice or receipt. The most important thing is to ensure is that any document, including an invoice or receipt, could not reasonably be seen as, 20. Making a record, or issuing or signing a certificate, report, or similar document that the member knows or ought to know is false, misleading or otherwise improper. [O.Reg 801/93 Professional Misconduct]
In cases where multiple members of a family are treated at different times and in different constellations, it would be reasonable to make a principled decision and apply the same logic whenever similar situations arise, regardless of the wishes of the particular client or what their insurance coverage allows.
In this particular case, if an intervention is intended to impart parenting skills to the parent, it might be reasonable to assume that parenting work is intended to help the parents change their behaviour and consider that the services were provided to the parents. This would be different than meeting with the parents in order to provide them with therapy progress information or information to help them support the work being done individually with the child.
Most of the time this question comes up in the context of a family with per-person insurance coverage limits. In situations like this, a parent may ask to revise invoices or receipts once a family member reaches their insurance coverage limit. One must be careful not to issue an invoice in a manner where it could be alleged that the person issuing the invoice was participating in something that could be seen as misleading.
Wherever possible, it might be helpful to ensure an invoice provides clear information about the nature of service and identifies those to whom the service was provided. If a person to whom the service was provided is different than the person who is the focus of the treatment, it may be appropriate to note on the invoice something like services were provided to Mr. and Mr. Smith re: the treatment of their child James Smith. Clients may also be asked to consult with their benefits providers about how to best maximize their coverage and the insurer’s preferences with respect to billing.
While it may feel helpful to assist clients in maximizing their insurance coverage, insurers are becoming increasingly vigilant about such matters and this could result in denial of benefits to the client and a complaint to the College. It should be left to the client(s) and their insurers to work out issues about insurance coverage limits.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 3 of HeadLines
This scenario presents some potential challenges.
Consent may be more complicated than might initially meet the eye. The clients in such a situation could decide to enter the relationship because of a perceived expectation by the therapist that they will agree and not want to disappoint the therapist by declining the invitation. For this reason, if this were to occur, such an opportunity would have to be presented in an entirely neutral manner.
To be fully informed consent, each client would have to be made aware of all the potential benefits and risks. These benefits would obviously include mutual support. On the downside, entering a relationship in which the client could be taking on further emotional (and perhaps other) demands should be presented as a risk to their own therapeutic relationship with the therapist and consequently to their therapeutic progress.
Confidentiality could also become a challenge when clients are introduced and encouraged to communicate. While each client would know that the other was seeing the same therapist, the therapist would have to be vigilant not to share any information about the other client without authorization. This would become difficult if they wished to talk about the other client or about interventions being used with them and it could become difficult to avoid inadvertently providing information, even in refusing to actively answer certain questions that could be posed. Even if information about one client was never disclosed to the other, the therapist would have to be vigilant about avoiding the collection of information about one from the other without consent. Even with full consent, collection of such information could pose challenges to professional objectivity, if information arose about any conflict arising between these individuals or any adverse information about them. This would become a dual relationship in the same way as working with clients who are relatives or friends of one another would, and it’s best to avoid dual relationships.
There are no specific prohibitions against introducing clients, but these are some of the challenges in managing such an intervention, without the safeguards of therapist mediated interaction between clients, as might occur in a therapist mediated mutual support group.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 3 of HeadLines
A member of the College with a Retired Certificate of Registration or a former member may not provide any psychological services of any kind. They would however, be able to provide information regarding services provided while holding a Certificate of Registration Authorizing Autonomous Practice. If, for example, the court required the client to be reassessed or needed testimony about matters not addressed while the member held a Certificate of Registration Authorizing Autonomous Practice, this would appear to be a new service and not one that should be provided unless one is authorized to provide psychological services.
The College is not in a position to require, and assure the public, that members with a Retired Certificate of Registration are maintaining their professional competence through continuing professional development. They are also not required to maintain their professional liability insurance coverage, which protects clients who may have a legitimate claim for financial awards as a result of a member’s professional activities. This is obviously also the case for retired members as well.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 4 of HeadLines
This question often arises when a member has been treating or assessing a client where the primary focus of clinical attention has not involved an assessment of the factors bearing upon the opinion being sought. This may occur, for example, when a member has conducted a psychoeducational assessment, or treatment for an anxiety disorder, and the member is later asked to provide information to be used in a parental rights matter. Another example is when a member has provided psychotherapy to address a client’s emotional disorder and is then asked to provide a letter regarding the individual’s readiness to return to work after an injury.
In providing professional opinions, a member must consider the following requirement in section 10.3 of the Standards:
10.3 Rendering Opinions
A member must render only those professional opinions that are based on current, reliable, adequate, and appropriate information.
In the first example above, a member should only provide information that they can reasonably expect to be used to determine custody or access arrangements if they have conducted an appropriate assessment for the purpose of determining child custody and/or access. Likewise, in the second example, a member should only opine on a person’s suitability to return to work after appropriate consideration of the person’s rehabilitation needs and the task requirements of the workplace.
Members must ensure that they work only within their authorized areas of practice and provide only those services in which they have the adequate knowledge, skill, and experience, within those authorized areas.
Even when a member is authorized and qualified to provide an opinion unrelated to the service they have been providing, and have conducted an adequate assessment, problems may arise if they assume a dual role. Usually, such requests for information are related to the rights and entitlements of the client. They also have an impact on others, such as family members, colleagues, or employers. A clinician who has not conducted an appropriate, objective assessment of the matter at hand can face challenges with respect to whether they have exercised sufficient neutrality. There may also be a perceived conflict of interest if it appears that a continued professional relationship could be endangered by offering an opinion that is seen to be unfavourable to the client’s interests.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue: 4 of HeadLines
Section 4.1.1 of the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 requires that:
8) the supervising member must ensure that billing and receipts for services are in the name of the supervising member, psychology professional corporation or employer and clearly identify the name of the supervising member and the name, relevant degrees and professional designations of the supervised psychological service provider
There is no explicit requirement under this Standard for there to be a signature, however, the following Standards are also applicable to these situations:
4.1.2 Supervision of Supervised Practice Members; and
4.1.3 Supervision of Non-Members
In addition to the responsibilities outlined in 4.1.1:
a) the supervising member must co-sign all psychological reports and formal correspondence related to psychological services provided by non-member supervisees;
Invoices (and receipts) would be considered by most to be “formal correspondence” and should be co-signed by supervisors.
Within the past few years, the College has received an increasing number of complaints about the transparency of such documents and what some third-party payers have alleged to be misleading practices by members. Increasing vigilance by third-party payers has, unfortunately, led to denial of insurance benefits for some clients. It has also led to an increased level of scrutiny of College members by claims adjusters. Supervisors should demonstrate that they carefully oversee the administration of their services by personally applying their own signatures to invoices issued in their names.
Originally published in Volume: 1 Issue 4 of HeadLines
In determining the appropriate record keeping requirements it’s important to consider what is meant by “consultation”. Sometimes, those using the title “consultant” are actually providing direct services to individuals. For example, this would be the case if the service involved interviewing clients of an agency and providing an assessment of their treatment needs. The member would, in such a situation, be required to create a client record in accordance with section 9.2 of the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017. Even if, by virtue of the administrative arrangements, the client is also a client of the agency and agency is the Health Information Custodian, the definition of client in the Standards is applicable:
Client: an entity receiving psychological services, regardless of who has arranged or paid for those services. A client can be a person, couple, family or other group of individuals with respect to whom the services are provided. A person who is a “client” is synonymous with a “patient” with respect to the administration of the Regulated Health Professions Act (1991).
If involvement in a case was limited only to discussing the client with the clinician providing the direct client care, it is more likely that the consultation met the definition provided in the Standards: Consultation: the provision of information, within a relationship of professionals of relatively equal status, generally based upon a limited amount of information that offers a point of view that is not binding with respect to the subsequent professional behaviour of the recipient of the information.
If acting as a consultant, as it is defined above, then the following requirements regarding contents of records apply:
9.3 Organizational Client Records
- A member must keep a record related to the services provided to each organizational client.
- The record must include the following:
a) the name and contact information of the organizational client;
b) the name(s) and title(s) of the person(s) who can release confidential information about the organizational client;
c) the date and nature of each material service provided to the organizational client;
d) a copy of all agreements and correspondence with the organizational client; and
e) a copy of each report that is prepared for the organizational client.
Even though the phrase “nature of” each material service, is not defined above, most prudent members record enough information to indicate the nature of the problem discussed and the nature of advice given.
Standard 9.4 provides the record retention requirements with respect to organizational records:
2) The organizational client record must be retained for at least ten years following the organizational client’s last contact. If the organizational client has been receiving service for more than ten years, information contained in the record that is more than ten years old may be destroyed if the information is not relevant to services currently being provided to the client.
Standards of Professional Conduct 2017
The Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 state that:
11.1 Fees and Billing Arrangements
Members must reach an agreement with an individual, group or organization concerning the psychological services to be provided, the fees to be charged and the billing arrangements prior to providing psychological services. Any changes in the services to be provided must be agreed to by the client before service is delivered or fees are changed. Fees must be based on amount of time spent and complexity of the services
rendered.
Practical Application: Fees for services should be determined on a consistent basis, regardless of the payer. A member may, however, offer pro bono services or apply a sliding scale to ensure access to services and affordability.
While this Standard is most often thought of in the context of initiating services with a new client, it also can be read to apply with respect to the ongoing provision of services. That is, “providing psychological services” could be read to mean each instance of providing a psychological service. It would be inappropriate for a client to learn that their fees had been increased when they receive a bill for a service that had already occurred. Increased fees may be an important consideration for clients in the ongoing informed consent to service process and some clients may need to reconsider whether they are able, or prepared, to continue at the new proposed rate.
There is no specific period of notice for a fee change set out in any Regulations or in the Standards as this is a matter of professional judgment. Adequate notice of the change however, is important and there may be clients who experience a fee increase as akin to indirect termination of therapy.
In cases where the client may not agree to an increased fee, and a member is not prepared to continue to provide services at the existing rate, guidance regarding the termination of services can be found in section 8 of O.Reg. 80.1/93: Professional Misconduct. This section of the Regulation states that termination of service that is needed is an act of professional misconduct unless:
i. the client requests the discontinuation,
ii. the client withdraws from the service,
iii. reasonable efforts are made to arrange alternative services,
iv. the client is given a reasonable opportunity to arrange alternative services, or
v. continuing to provide the services would place the member at serious personal risk.
Although there are informal ‘rules of thumb’ with respect to ‘winding down of therapy’, often based upon the length of time a person has been receiving treatment, the College does not set any particulars in this regard. If the client requires additional services but can not or will not pay the increased rate, it would be reasonable and appropriate to work with them for a time period that, in the member’s professional judgment, is sufficient to arrange for a transfer of care to another service provider and avoid any harm due to a disruption of treatment.
Introduction
The College has received many questions from members of the College and the public about the Controlled Act related to Psychotherapy since it was proclaimed on December 30, 2017.
Members of the College of Psychologists are permitted to perform the Controlled Act related to Psychotherapy, so members need not be concerned whether psychotherapy they provide falls within the definition of the Controlled Act. As always, members are responsible to ensure that they are competent to provide any psychological service they offer. The definition of when services fall within the Controlled Act becomes much more important when one is considering supervising someone in the performance of the Controlled Act.
Information currently available on the College website may address some of the member inquiries. This can be found in the Practical Applications to the Standards of Professional Conduct, 2017 in the Standards of Professional Conduct.
Further information is available and in the Questions and Answers document accompanying the Standards
The following information is intended to address the most frequently asked Questions the College has received. If there are other questions, you please email them to practiceadvice@cpo.on.ca.
Definitions
The Controlled Act related to Psychotherapy is defined in section 27(2) of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 (RHPA) as:
14. Treating, by means of psychotherapy technique, delivered through a therapeutic relationship, an individual’s serious disorder of thought, cognition, mood, emotional regulation, perception or memory that may seriously impair the individual’s judgement, insight, behaviour, communication or social functioning.
The legislation does not define the terms used in this definition particularly “psychotherapy” and what is meant by “serious”. Within the Psychotherapy Act, 2007 however, the ‘practice of psychotherapy’ is defined as:
3. the assessment and treatment of cognitive, emotional or behavioural disturbances by psychotherapeutic means, delivered through a therapeutic relationship based primarily on verbal or non-verbal communication.
The legislation does not define “serious” with respect to what is a “serious disorder . . . that may seriously impair”. This is left to the treatment provider to apply his/her own education, skill, and training to determine. As noted above, this need not be of concern to members personally offering psychotherapeutic services as members of the College are authorized to perform this Controlled Act. It is important, however, when one is considering providing supervision. In the absence of any available jurisprudence defining these terms within the definition, especially as related to a “serious disorder . . . that may seriously impair” members of the College are expected to exercise their professional judgment in deciding whether the services which they contemplate supervising constitute the Controlled Act.
Whether an activity constitutes the Controlled Act requires consideration of the level of difficulty and potential impairment experienced by the client and is not dependent on a specific diagnosis or therapeutic modality.
Members who are not comfortable exercising their own professional judgment in deciding whether a service falls within the “serious disorder . . . that may seriously impair” definition of the Controlled Act should consult with another member, another regulated colleague authorized to perform this Controlled Act or seek legal advice.
Questions and Answers
1. Is the provision of all “psychotherapy service” now controlled by the new legislation?
No. As noted in the definition, only psychotherapy delivered to a client with a “serious disorder . . . that may seriously impair” their functioning falls within the Controlled Act.
2. In general, under what circumstances may I supervise the performance of the Controlled Act?
Most of the concerns raised are related to supervision by College members of others who are performing the Controlled Act. The RHPA specifically sets out that a person who is not yet authorized to perform the Controlled Act independently may do so under supervision but only if she/he is fulfilling the requirements to become a member of a health profession, the act is within the scope of practice of the profession and is done under the supervision or direction of a member of the profession [emphasis added].
It is important to note that College members may continue to supervise individuals they believe have the competence to provide psychotherapeutic services when those services fall outside of the Controlled Act.
3. With regards to performing the Controlled Act of psychotherapy, may I supervise:
a) Doctoral psychology students in practica or internship placements or individuals is in the process of obtaining their four years of supervised experience necessary to apply to become a psychological associate?
The legislation permits one to supervise individuals who are fulfilling the requirements of our College. This includes supervised practice members, students in practica or internships as well as those gaining their required post-masters experience.
b) Autonomous practice members of the College who may require supervision to expand their authorized areas of practice or their authorized population groups or who require supervision pursuant to a decision of the Inquiries, Complaints and Reports Committee (ICRC) or Discipline Committee?
Yes. Given that one is permitted to supervise a Supervised Practice member as noted above, it would seem inconsistent with the intention of the legislation for members not to be able to supervise another autonomous practice member to meet College requirements to practice in specific areas or with specific populations or fulfill a condition required by the ICRC or Discipline Committee.
c) Autonomous practice members of the College who may wish to increase their psychotherapy skills within their authorized areas of practice or their authorized population groups?
Generally, these members would become involved in a mentorship, consultation or training relationship, rather than a formal supervisory one. Since they are already authorized in the area or with the population, the College does not require supervision when a member is learning new techniques or increasing the scope of their activities within their authorized areas.
d) Individuals who are in the process of becoming a member of the College of Registered Psychotherapists of Ontario (CRPO) or another College whose members are authorized to perform the Controlled Act?
On December 21, 2017, the Minister of Health and Long-Term Care announced that, “Individuals who provide these services [the controlled act] will have a two-year transition period, beginning December 31, 2017, to register with a regulatory college.” Therefore, supervision of individuals in the process of becoming a member of the CRPO or another College whose members are authorized to perform the Controlled Act is permitted as follows:Transition Period to December 31, 2019:
The transition period appears to permit individuals to perform the controlled act whether or not they are under supervision. In keeping with the apparent intention of the transition period, that is to provide an opportunity for individuals to register with a relevant regulatory College; the College is of the view that it would be appropriate to permit members to supervise individuals who are preparing to become a member of the CRPO, during the transition period.It is important to note that there is no restriction with regard to College members offering training, support, consultation and mentorship to other practitioners. While the CRPO may use the term “supervision” in their requirements for candidates, their use of the term may connote a less formal arrangement than that outlined in Principle 4 of our Standards. Individuals seeking registration with the CRPO should inquire of their College if a mentorship, training or consultation relationship, rather than a formal supervisory one, as defined by our College, may satisfy the requirement. In agreeing to consult, the College would expect members to inform CRPO qualifying members that they should not indicate to clients that they are being ‘supervised’ as this could be misleading and suggest a degree of responsibility by the College member which is inaccurate. Rather it would be appropriate for them to explain that they are seeking consultation and training from a member of our College.
Post Transition Period:
The legislation only permits one to supervise individuals who are fulfilling the requirements of their own College, in our case, the College of Psychologists. Therefore, after December 31, 2019 one cannot provide supervision, as it is defined by the College, to individuals who are becoming members of another College.As noted above, there is no restriction with regard to College members offering training, support, consultation and mentorship to other practitioners. While the CRPO may use the term “supervision” in their requirements for candidates, their use of the term may connote a less formal arrangement than that outlined in Principle 4 of our Standards. Individuals seeking registration with the CRPO should inquire of their College if a mentorship, training or consultation relationship, rather than a formal supervisory one as defined by our College, may satisfy the requirement.
e) Members of another regulated health profession who themselves are authorized to perform the controlled act?
Yes. If these individuals are authorized by their own College to perform the controlled act, they can do so independently or under the supervision of a member of the College of Psychologists. As with members of the College of Psychologists who are authorized to perform the Controlled Act [as per 3.c) above], in most circumstances it may be appropriate to establish a non-supervisory relationship that would afford them training, support, consultation and mentorship. If, however, there is a reason that non-supervisory supports would be insufficient, and supervision is necessary, a member of the College may enter into a supervisory relationship as outlined Principle 4 of the Standards.
4. Are there any circumstances when a member may supervise others in providing services, including performance of the Controlled Act, because a third-party payer will only cover services if they are supervised by a Psychologist or Psychological Associate?
Supervision of the controlled act of psychotherapy or any other psychological service may not be undertaken solely to facilitate third-party payment [Standards of Professional Conduct 4.1.1 (6)].
5. May I supervise a Registered Psychotherapist or Social Worker in services which fall outside of the definition of the Controlled Act?
Yes. You are permitted to supervise activities that fall outside of the definition of the Controlled Act by a Registered Psychotherapist or Social Worker or anyone else that you believe has the education, training and experience to provide those services under your supervision.
6. Can exceptions to the restrictions on performance or supervision of the Controlled Act be made for clients who require services in remote communities or who would be affected because a therapist is no longer eligible for supervision?
The legislation does not provide for any exceptions and the College cannot recommend or condone any activity that would not be permitted by legislation. In assuming responsibility for the supervision of a psychological service, the supervisor has taken on responsibility for the client’s care. Where a supervisee is no longer able to provide the supervised service, the supervisor may provide client care him or herself, or help the individual to find another competent practitioner from whom they can receive services.
The College has not set out specific, concrete age boundaries between the various client populations: children and adolescents; adolescents and adults; adults, and seniors. One usually goes by conventional definitions. That is, children to age 12 or 13; adolescents to age 19 or so; adults to 65 or 70. While age is not an issue when considering providing service to a client who falls within these conventional age groups, problems can arise at the boundary ages, i.e., 12-13; 18-20; 65-70. When determining whether it is within one’s area of competence to provide service to a “boundary age” individual, many things other than just chronological age come must be considered.
The concern that arises should a member, with demonstrated competence in working with adults, decide to provide service to an older, boundary age adolescent is that one may impart to the older adolescent some adult traits, characteristics, or difficulties based on one’s training and experience. Conversely, a member may not recognize some adolescent trait, as one is approaching the client from an “adult” perspective. Issues can also arise with the use of assessment measures and intervention techniques as one may be most familiar with both the objective and subjective norms related to working with adults.
The Registration Regulation (O. Reg. 74/15) requires that members practice the profession only within those areas of the member’s competency that are authorized by the College [s. 10 (2) 1.] There is some room at the boundary ages, however, for a member to provide service to a client who might fall, by convention, just outside of one’s authorized population group. Whether a member is practicing within one’s area of competency, as required by the Regulation, is a determination a member must make on a case by case basis, based on the characteristics of the individual client.
A member whose area of competence is Clinical Psychology with adults may occasionally see a boundary age adolescent (18-20 age range), who many might consider a young adult, dependent upon the evaluation of his/her level of development and maturity. It is important to stress however, that should such requests for service become a more regular occurrence, it would be prudent for the member to one consider expanding one’s authorized population groups.
While the above information relates to a boundary age adolescent and a member whose area of competency is with adults, the principles can be applied to a member considering providing psychological service to the other boundary age client groups.
You’ve asked about situations in which you are being required to act in contravention of the Standards. The Standard requiring best efforts to affect change in the workplace relates to situations in which others in the workplace are doing things that contravene the Standards.
When attempting to address the conduct of others in the workplace, Standard 3.1.2 does require you to make the best efforts to ensure that your work setting adheres to the Standards.
If your efforts to change the behaviour of others at work meet resistance, best efforts could include presenting additional information that supports a compelling argument for the changes, writing a formal memo to those in a position to modify policies, or escalating the issue to a higher level in the organization. You would not be expected to take steps like resigning from your position and losing your livelihood, as this would be considered undue hardship.
It is different if you, as opposed to others in the organization, are required to contravene the Standards, as a failure to comply with the Standards, yourself, would constitute Professional Misconduct. For example, if an employer were to ask you to provide services outside of your authorized areas of practice and/or competence, without the opportunity for supervision, you would not be permitted to so under any circumstances.
Fortunately, it is in the best interests of most employers to support ethical practice and most of the time it is possible to affect change. If you are unable to resolve this problem with your employer on your own, it may be necessary to seek independent legal advice to discuss your range of options.
Please don’t hesitate to contact the College’s Practice Advisory service if you’d like to discuss any specific situations like the ones described above.
The Supervision standards apply to the supervision of all psychological services and psychological research is deemed to be a psychological service. In the public interest, it is important to ensure that research is conducted ethically and that it produces reliable and valid information.
Some activities which non-members perform in the course of assisting with research may not require supervision if one would not need professional education, training, and/or experience in order to perform them. For example, tasks like administratively providing and collecting self-administered questionnaires may be performed without the supervision of the nature required by the Standards. Tasks which do require professional education, training, and/or experience, like interactive administration of tests and/or interpretation of subjects’ responses, would require supervision in the manner set out in the Standards.
If you do not wish to take on the responsibilities of a supervisor, you would need to ensure that he would be satisfied with your acting as a consultant and/or trainer, but not as a supervisor as defined within the Standards of Professional Conduct for members of the College of Psychologists of Ontario. You’d have to have an agreement with him that makes it clear that you are not clinically responsible for the casework, that it’s his responsibility to evaluate any information you are providing to him and that he would need to make his own independent decisions about whether to heed any advice you give. In the event that he requires someone to assume clinical responsibility for his services, you must make it clear to him that by consulting and/or training you would not be assuming responsibility for client care.
Your question suggests that you would be supervising another professional’s “practice”. It is important to remember that clients seen under your supervision are actually considered to be your own clients and, as such, you should consider them as clients of your practice and not the supervisee’s.
There is no specific prohibition against supervising another professional with respect to the care of some individuals, without supervising the care of all of the individuals they work with. It can, however, be challenging to ensure that all of those concerned are aware of which activities you are supervising and which ones you are not. In addition to complying with the Standards relevant to supervision, you would have to be mindful of adhering to all of the other relevant Standards, including:
6.4 Public Announcements
Public announcements of psychological services and fees must be offered in the name of an
autonomous practice member of the College.
This means that you may not permit a supervisee to advertise the services which you supervise under his or her own name, and must instead advertise the supervised services as part of your own practice.
9.1.2 Members Responsible for Supervising Supervised Practice Members and Non Members
Members supervising Supervised Practice members and non-members are responsible for the security, accessibility, maintenance and retention of records.
This means that you must ensure that you have full control over the records of those clients whose services you supervise, and take possession of those files when the supervision (and your authority) ends.
11.1 Fees and Billing Arrangements
A member must reach an agreement with an individual, group, or organization concerning the psychological services to be provided, the fees to be charged, and the billing arrangements prior to providing psychological services. Any changes in the services to be provided must be agreed to by the client before the service is delivered or fees are changed. Fees must be based on the amount of time spent and complexity of the services rendered.
This means that you must be directly involved in all agreements for services, as well as fees and billing arrangements, prior to the supervisee beginning to provide service or before arrangements are changed.
All of the information above applies, regardless of whether the supervisee is a member of another health regulated profession if you are supervising them in the provision of psychological services.
Autonomous practice members wishing to add an area of practice or a client group must undertake training and supervision to achieve competency comparable to other members of the College who are recognized for similar practice.
Members are required to make a written request to the Registration Committee specifying the practice area or client group they wish to add and to provide detailed information about how they have or plan to acquire the knowledge and skills in this new area.
The College’s Guidelines for Change of Area of Practice, outline the process in more detail.
The Registration Committee meets approximately every other month, dates of upcoming meetings are posted on the College’s website.
The question of the release of raw test data involves an understanding and interpretation of the Personal Health Information Protection Act (PHIPA) which speaks to responding to requests for personal health information. It should be noted that the College does not provide legal advice or legal interpretations of legislation but recommends that members seek legal advice on such matters. While not providing legal advice, the College does offer some comments which may be helpful in understanding this question and informing the discussions with legal counsel
The Personal Health Information Protection Act (PHIPA) gives a client, or legal guardian, the right of access to, or the right to consent to the disclosure of, his/her personal health information. This would include much of the information in the psychology file. There are some exceptions, however, to this right. These include information that could pose a risk of harm and confidential third party information. As well, “raw test data from standardized psychological tests” [PHIPA 51.(1)] is excluded from this right. Therefore, the legislation does not appear to provide a right to access raw data.
In considering PHIPA 51.(1), it is important to recognize the distinction between a right and a permitted disclosure. There does not appear to be any statements in PHIPA that prohibit the release of “raw test data from standardized psychological tests”. The difference to be understood is between what the client may have a right to obtain, and what they may be permitted to receive. In this regard, the legislation is permissive, rather than prescriptive.
Recognizing this permissive language in the legislation, the College position related to the release of raw test data may be found in Principle 10 – Assessment and Intervention of the Standards of Professional Conduct; specifically section 10.8. This section notes that the College recommends that when the request is reasonable and appropriate, and with proper authorization, the raw data should be released to clients and others.
It is important to note that Principle 10.8 emphasizes the member’s responsibility to distinguish between raw test data from standardized psychological tests and test materials or forms. This suggests that test protocols, test items, summary sheets, etc., most of which are materials copyrighted by the publisher, should not be reproduced based on voluntary consent. Rather, one may have to recopy the information ensuring not to include any copyrighted materials. Of course, should one receive a court order, summons to appear and bring materials to court, or some other legal vehicle compelling the release of the entire file, then this could also include the raw test data protocols. In such cases, members are encouraged to consult with legal counsel and/or the test publisher.
The Standards relevant to supervision are only applicable to the supervision of psychological services. If your supervisory role is strictly administrative and you only do such things as approve vacation time, arrange scheduling or perform other human resources-related activities, then you would not be subject to the requirements for supervisors of psychological services. If you do supervise activities that would fall within the scope of practice of psychology, then you are required to adhere to the Standards regarding the supervision of psychological services.
Section 3 of the Psychology Act, 1991 defines the practice of psychology as:
… the assessment of behavioral and mental conditions, the diagnosis of neuropsychological disorders and dysfunctions and psychotic, neurotic and personality disorders and dysfunctions and the prevention and treatment of behavioral and mental disorders and dysfunctions and the maintenance and enhancement of physical, intellectual, emotional, social and interpersonal functioning. 1991, c. 38, s. 3.
In Canada, the practice of psychology is regulated at the provincial/territorial level. That is, each province/territory is responsible for the regulation of psychological services delivered within its borders. Within the United States, psychology is similarly regulated.
At this time, most jurisdictions regulating psychology in Canada and the US, including the College of Psychologists of Ontario, view services to be delivered in the province/territory/state in which the client is located whether such service is provided in person or through telepsychology. That is, the service is deemed to be provided where the client is, regardless of where the psychologist or psychological associate may be located. Given this, many regulatory bodies expect the practitioner to be registered/licensed in the jurisdiction in which the service is being provided.
At this time, there is some variability in the expectations of the various Canadian jurisdictions with regard to what is required of a practitioner providing services by telepsychology into their province/territory. Some may have temporary or courtesy registers which permit a member to practise within their jurisdiction for a limited period of time without formal registration with them. For members considering providing service by telepsychology into another jurisdiction, it is recommended that they contact the regulatory body of the jurisdiction into which they may be considering practising to determine what may be required of them in terms of registration/licensing or formal notification of the regulatory body for psychology. The College of Psychologists of Ontario has adopted, as advice to members, the Model Standards for Telepsychology developed by the Association of Canadian Psychology Regulatory Organizations (ACPRO). In addition, a joint task force of the Association of State and Provincial Psychology Boards (ASPPB), the American Psychological Association (APA) and the American Psychological Association Insurance Trust (APAIT) has recently developed Guidelines for the Practice of Telepsychology. The Canadian Psychological Association has also published Draft Ethical Guidelines for Psychologists Providing Psychological Services Via Electronic Media.
Members considering providing telepsychological services will find these documents very useful as they provide guidance on a variety of issues related to this type of service. This includes ensuring one is legally entitled to practise in another province, territory, or state and one is familiar with the relevant laws and regulations applicable within that jurisdiction.
If you are supervising the psychometrist, then a supervisory agreement is necessary. In institutional settings, such as school boards, hospitals, and correctional facilities, if your employment contract and the supervisee’s employment contract both address the required terms of supervision referred to in the Standards, this would be considered to constitute a supervision agreement.
If you are supervising psychological services, the public is entitled to rely on an expectation that the services delivered will meet the standards of the profession.
There are unregulated professionals providing many services in Ontario, including behavioural intervention, counselling, and rehabilitation therapy. These professionals may be providing competent and ethical work but they are not subject to rigorous entry to practice requirements, standards of conduct to comply with, mandatory quality assurance requirements or a complaints mechanism to address concerns that may arise about the services. When a College member is supervising the provision of any psychological services, the College and its members have an obligation to the public to ensure that the services meet the same standards as they would if delivered directly by the member.
Many of the elements of a supervision agreement listed within the Standards apply broadly to any situation in which supervisors take responsibility for the work done by their supervisees. Some elements of Standard 4.1.1 (5) which may be applicable to the supervision of research and other non-clinical activities include:
a) the date upon which the agreement is effective and the expected date upon which it will expire;
b) the specific duties and obligations of the supervisee;
c) any limitations imposed upon the activities of the supervisee;
d) the specific duties and obligations of the supervisor;
e) the expected frequency and length of supervision meetings;
g) contact information and emergency contact information for both the supervisor and supervisee;
h) confirmation that the supervisee will comply with all requirements under the legislation and regulations relevant to the service and the Standards of Professional Conduct (2017); and
i) identification of a plan for appropriate support for the supervisee in the event of the supervisor’s unavailability.
In institutional settings, such as Universities and hospitals, employment contracts that address the terms of supervision referred to in these Standards may be considered to constitute a supervision agreement.
Many of the elements of supervision records listed within the Standards apply only to the care of clients. Some, however, apply more broadly to any situation in which supervisors take responsibility for the work done by their supervisees. Some elements of Standard 4.1.1 (3) which may be applicable to the supervision of research and other non-clinical activities include:
a) the date and length of time of each supervision meeting;
d) a summary of discussions regarding any relevant ethical, professional and jurisprudence issues discussed at each supervision meeting;
e) a notation of any directives provided to the supervisee at each supervision meeting; and
f) a notation of any of the supervisee’s strengths and needs for further development identified at each supervision meeting;
A supervisor would be expected to make a record of any relevant ethical, professional, and jurisprudence issues discussed, directives provided, and strengths and needs for development identified during a supervision meeting. If few or none of these things were discussed at a particular meeting, then only a very brief notation including only the date and length of the meeting would be required.
The Standard is intended to ensure that there is clear agreement between the supervisor and supervisee with respect to all of the minimum elements listed in the Standards. It may be onerous to individuals make agreements that are redundant. So long as it can be demonstrated that each individual supervisor and supervisee has agreed to all of the following elements, whether directly or through a third party, you could consider that there is an agreement which meets the Standards:
a) the date upon which the agreement is effective and the expected date upon which it will expire;
b) the specific duties and obligations of the supervisee;
c) any limitations imposed upon the activities of the supervisee;
d) the specific duties and obligations of the supervisor;
e) the expected frequency and length of supervision meetings;
f) the manner in which the supervisor will be directly involved in the planning, monitoring and evaluation of the services provided to clients;
g) contact information and emergency contact information for both the supervisor and supervisee;
h) confirmation that the supervisee will comply with all requirements under the legislation and regulations relevant to the service and the Standards of Professional Conduct (2017); and
i) identification of a plan for appropriate support for the supervisee in the event of the supervisor’s unavailability.
To the extent that any of the minimum elements of an agreement listed above are not addressed, an additional agreement covering the missing elements would be required.
Because of the diversity of supervision and consultation arrangements members are involved in, the College could not possibly provide examples or templates of agreements that would cover every situation.
We encourage you to design agreements that make sense for your own particular practice that contain at least the minimum information specified in the Standards. You are also free to add any additional elements you consider important in an agreement and may use any kind of language you wish to use.
If it would help to see how some similar agreements are structured, here is a link to a few sample supervision contracts online: http://www.cfalender.com/supervision-contracts.html. These may or not be relevant or appropriate for all kinds of relationships but may provide a sense of what others’ agreements look like.
Although the Standards require you to record information that will permit the identification of each client, there is no need to use full client names, as long as it is possible for you to associate these identifiers with the clients should you need to. The use of coded names would prevent the release of unnecessary personal health information about clients to those reviewing a file for purposes related only to the supervisee.
Examples of appropriate references to clients in a supervision file include: “Discussed Interpretation of Test Scores for A.L. and asked Supervisee to correct tabulations and reinterpret with new scores” or “Discussed Supervisee’s own reaction to N.Q.’s disclosure, Supervisee discussed own discomfort with this issue and we generated a list of other possible responses, including seeking more information or waiting for the client to reflect before problem-solving. Will discuss Supervisee’s reactions to client information again following N.Q’s next session.”
When a client makes a request for his or her record, or authorizes release of it to another person, subject to the specific exceptions in privacy legislation, you must comply with the request. All information about a client that is relevant to the services provided should, however, be contained within the client record. There should be no information relevant to client care in a supervision record that would not also be found in the client’s own file.
A supervision record should contain only information relevant to the member’s supervision of the supervisee’s performance, developmental goals, progress, and challenges. It should only include incidental reference to clients to relate the narrative to specific cases.
If for any reason, you are compelled to provide a supervision record because it contains information related to a client, it would be important to ensure that information about other clients recorded in the supervision record is not disclosed without their consent or unless you are legally compelled to release it. Similarly, you should not release personal information about the supervisee without the supervisee’s consent, unless you are legally compelled to release it.
If faced with a request which leads you to believe that supervision records are specifically being sought, you may indicate that the supervision records pertain to the supervisee’s own developmental goals, training, and growth, that all client-related information is incidental to these issues, and that all client-related information is contained in the client file. Again, unless required by a court of law, you must not release supervision records unless both the supervisee and client specifically authorize you to do so.
You may supervise anyone you believe has the competence to provide services under supervision, so long as they are not performing one of the Controlled Acts as listed and described in the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991, which include: communication of a diagnosis; applying or ordering the application of a form of energy; and, once proclaimed in force, the Controlled Act of Psychotherapy. As counselling is not a controlled act, there is no requirement that they be registered, or seeking registration, in a College.
Consultation is defined in the Standards as:
… the provision of information, within a relationship of professionals of relatively equal status, generally based upon a limited amount of information that offers a point of view that is not binding with respect to the subsequent professional behaviour of the recipient of the information.
Supervision is defined as:
…an ongoing educational, evaluative and hierarchical relationship, where the supervisee is
required to comply with the direction of the supervisor, and the supervisor is responsible for the actions of the supervisee.
In providing exclusively training and advice to other professionals, it is more likely that you are providing consultation than supervision. If this is the extent of your involvement with these individuals, adherence to the requirements under section 4.1.5., which involves clarification of the limits of your involvement as a consultant, would be sufficient and appropriate.
Your question indicates that you ‘have some input into the administration of tests and counselling’. If your input involves only making recommendations to other practitioners who take responsibility for the decision about whether to accept the recommendations, this would be consistent with the role of a consultant. If, however, “input” means directing which tests and counselling interventions will be used, and the recipients of the input are required to follow your directions, it may be that you are providing supervision and would be bound to adhere to the Standards regarding supervision of non-regulated professionals. If you are interpreting test results yourself, then you are considered to be actually providing a psychological service to the clients, and you are expected to adhere to all of the Standards which apply to the direct provision of psychological services.
Providing training does not necessarily make a relationship supervisory. A relationship in which you have been specifically asked to provide training, or a consulting relationship which may have a training component, only becomes a supervisory relationship if it becomes evaluative and hierarchical and when the person receiving information from you is required to do as you instruct. In the kind of consultation situation, you have described it is particularly important to ensure that an agreement makes it clear that you are not taking on responsibility for client care and that that responsibility is exclusively the consultee’s.
Making case specific recommendations to behavior therapists, advising with respect to the development of processes, and discussing general issues, are activities which are consistent with the role of a consultant, so long as it is understood that the recipients of the recommendations and advice are fully responsible for deciding whether to implement your recommendations.
If you are in a relationship with the behavior therapists that is educational, evaluative, and hierarchical, and they are required to comply with your direction, you would be considered to be supervising them.
Consultants are typically in the role of an external contributor to case discussions, where the recipients of the consultant’s ideas are free to either accept or reject them. If you are in the role of a consultant, while you may be providing advice to those making decisions about client care, you should not actually participate in making the decisions (e.g., “have a vote”), even when the responsibility for decision-making is shared.
Consultation is defined as:
… the provision of information, within a relationship of professionals of relatively equal status, generally based upon a limited amount of information that offers a point of view that is not binding with respect to the subsequent professional behaviour of the recipient of the information.
If this description fits your role with respect to the treatment team then it is likely that you would be considered a consultant and are required have a clear and formal agreement delineating responsibility for client care which spells out that the person receiving your consultation retains full responsibility for client care, in accordance with Standard 4.1.5.
If you are a participant in the actual clinical decision making with respect to the clients, as opposed to being simply a resource for the decision-makers, then you are more than a consultant and have the same obligations as any member of the College providing services to a client, in a way that is analogous to an assessor or file reviewer who does not provide intervention but must comply with all of the Standards with respect to client care.
There is no reason you cannot have an agreement that multiple parties can sign onto, so long as it includes everyone with whom you require an agreement. You could update this agreement whenever someone joins or leaves the team.
It would be reasonable to understand “formal” in this context to mean that contacts with the consultee(s) have been arranged, or are expected to occur in the future, specifically for the purpose of consultation, where consultation is defined as:
… the provision of information, within a relationship of professionals of relatively equal status, generally based upon a limited amount of information that offers a point of view that is not binding with respect to the subsequent professional behaviour of the recipient of the information.
This would be different than the regular discussions which frequently occur between professional peers on either an ad hoc basis or at team meetings or case conferences. It would be reasonable to consider a consultation arrangement to be “ongoing” if the participants expect to have future contact for the purpose of consultation.
If all members of the discussion are simply exchanging ideas, and you were not designated to make specific recommendations to others by virtue of your specialized expertise, it would not be considered “consultation”, which is defined as:
… the provision of information, within a relationship of professionals of relatively equal status, generally based upon a limited amount of information that offers a point of view that is not binding with respect to the subsequent professional behaviour of the recipient of the information.
Rather, it could be simply understood as team discussion or team development.
If, however, a relationship is established with specific individuals or groups, where you are identified as a person who is designated to provide advice or information regarding psychological matters, and there were plans for you to meet with them to provide advice or information more than once, then it would be considered to be formal, ongoing consultation.
There have been no changes to the Standards with respect to members limiting their services to their authorized client populations. We have tried, in revising the Standards, to make more members aware of the advice we provide about both the limits to authorized client populations and authorized areas of practice.
Members are still required to limit their services to their authorized populations and areas of practice. The College has never set age cutoffs, with the belief that members will use good judgment to determine whether a person is a child, adolescent, adult, or senior. Those distinctions should be based upon whether, in the member’s judgment, the client’s abilities, life situation, and challenges are consistent with those commonly associated with a particular group. We’ve provided some examples in the Practical Applications to Standard 5.1 contained within the Standards.
If you are not authorized to work with seniors, it would not be appropriate to take on a client facing age-related mental health challenges such as cognitive decline or social isolation.
If deciding whether to continue ongoing treatment with a client who has recently begun to experience the adverse effects of old age, it would be a good idea to refer him or her to someone authorized to work with seniors and, until this has occurred, seek consultation from someone with the specific training, skills and experience and who is authorized to work with seniors.
If an existing client is at a chronological age when age-related difficulties could reasonably be expected but are not yet occurring, it may be reasonable to still consider the client an “adult”. For example, if the client continues to work productively, live independently, has a vigorous fitness routine, is free from age-related health concerns, has meaningful and satisfying close relationships, etc., he or she need not be categorized as a “senior” for the purposes of the Standards, even if his or her age exceeds a commonly applied age marker such as 65.
The clients receiving services directly from your supervisee are considered to be your clients. As such, the client file is actually yours even while in the possession of a supervisee under your direction; this is the case with respect to files of clients seen by members of the College with Certificates of Registration Authorizing Supervised Practice as well as non-members of the College. You may decide that, rather than keeping client files in your possession while services are being provided, your supervision would extend to ensuring that the supervisee maintains the files in a secure, confidential and accessible manner, in accordance with the Standards and the applicable legislation. When the supervision period ends, the record of services which you had always been responsible for remain your responsibility. Given that you will not have authority over the conduct of the former supervisee, you must personally ensure that the records remain secure, confidential and accessible in the manner required by the Standards.
The Standards do not specifically prescribe what you must do with supervision files when you leave an organization in which you are providing supervision. In most cases, supervision of services to the clients of the organization would be considered an activity of the organization which is performed by the supervisor. If this is the case, the file likely belongs to the organization and it would make sense for the file to be left in the organization’s care and dealt with in accordance with the privacy legislation applicable to the organization. It is important to make the best efforts in these situations to ensure that the organization will retain the files for at least two years, as this is the prescribed retention period for supervision files when they belong to individual members who are not carrying out supervision in an organizational context. To use the analogy of a human resources file, if you would leave a human resources record with the organization in which you managed staff, then it’s likely that you would be expected to leave the record of supervision with the organization within which the supervision was provided. With respect to any information about an identifiable client in the files, the organization would, in most cases, be considered the Health Information Custodian and would be responsible for ensuring that the requirements of the Personal Health Information Protection Act are met.
The prohibition against fee splitting has been removed from the Standards but the prohibition against paying for referrals remains in force. The Professional Misconduct Regulation still strictly prohibits:
- Receiving or conferring a rebate, fee or other benefit by reason of the referral of a client from or to another person (Section 1.26)
Many people found the language used to address the practice of fee splitting in the previous version of the Standards difficult to understand. The College decided that concerns underlying the former specific fee splitting rule are already adequately addressed within the Professional Misconduct Regulation, which prohibits:
- Providing a service that the member knows or ought to know is not likely to benefit the
Client (Section 1.9); and - Practising the profession while the member is in a conflict of interest (Section 1.10);
and by the following requirements which have been carried forward from the previous Standards to the new ones:
- Fees must be based on the amount of time spent and complexity of the services rendered (section 11.1); and
- A member must not exploit persons over whom he/she has supervisory, evaluative, or other authority such as clients, students, supervisees, research participants, or employees (section 13.4(2)).
As a supervisor, you are providing a psychological service and it is important that your own fee structure for this service complies with the requirement that your fees are based on the amount of time you spend providing the service and the complexity of the service you are providing. Charging a percentage of fees collected or the number of sessions a supervisee has with a client may not correspond to the amount of time you are providing supervision. Charging a flat fee for a time period, without regard to the specific number of hours spent within that time period, would also be inconsistent with the standard and would have the potential to also violate the prohibition against exploitation of supervisees (section 13.4(2), as a supervisee could possibly be charged for supervision which was out of proportion to the time spent.
The prohibition of fee splitting was difficult to understand and misunderstood by many, so it was decided that, because concerns about the adverse consequences of fee splitting are addressed elsewhere in the Standards and the Professional Misconduct Regulation, that the Standard regarding fee splitting would be omitted from 2017 version.
The Professional Misconduct Regulation still strictly prohibits:
-
Receiving or conferring a rebate, fee or other benefit by reason of the referral of a client from or to another person (Section 1.26)
-
Providing a service that the member knows or ought to know is not likely to benefit the client (Section 1.9); and
-
Practising the profession while the member is in a conflict of interest (Section 1.10)
Additionally, the Standards still require that:
-
Fees must be based on the amount of time spent and complexity of the services rendered (section 11.1); and
-
A member must not exploit persons over whom he/she has supervisory, evaluative, or other authority such as clients, students, supervisees, research participants, or employees (section 13.4(2)).
As long as the practice you are describing does not occur in a supervisory relationship and your practice is compliant with respect to all of the above, you are now able to enter into percentage based arrangements.
The College has adopted the Association of Canadian Psychology Regulatory Organizations (ACPRO) Model Standards for Telepsychology Service Delivery. The Model Standards define Telepsychology as “the use of information and communications technology to deliver psychological services and information over large and small distances”. Practice within psychology using this modality would include all client-centered services, consultation, supervision of students/professionals/colleagues, and the education of the public and/or other professionals delivered to individuals outside of Ontario.
A telephone (landline or mobile) would be considered “communications technology”. While some of the items within the “Use of Technology…” section of the Standards may not be relevant to simpler, older technologies, some items would be relevant and applicable to even ‘lower-tech’ devices, including a corded or land-line telephone. Examples of requirements applicable to the use of all technologies in service provision would include the need to obtain authorization from the relevant jurisdiction before providing services to someone who is located outside of Ontario, ensuring the privacy of the person you are communicating with, and having contingency plans in the event of a technological failure.
For Employers, Insurers & Third Party Payers
There has been some confusion with respect to who may provide psychological services in Ontario and who may bill for such services. This information is provided in an effort to clarify any misunderstandings related to these issues.
To practise psychology in Ontario, an individual must hold a current certificate of registration from the College of Psychologists of Ontario; the regulatory body for the profession of psychology. Under the authority of the Regulated Health Professions Act, 1991 and the Psychology Act, 1991, the College registers two classes of autonomous practitioners: Psychologists and Psychological Associates.
A Psychologist or Psychological Associate who holds a Certificate of Registration Authorizing Autonomous Practice may provide services without supervision, within his or her area of competence, and may bill for these services. While most members of the College have no explicit term, condition, or limitation on their certificates of registration, some do and must practice in accordance with any such restriction.
To qualify for professional registration to practise psychology requires successful completion of:
- Rigorous educational and training requirements;
- Acceptable supervised professional experience;
- A standardized written examination that evaluates comprehensive knowledge in psychology and is used throughout Canada and the United States;
- A written examination that evaluates the candidate’s ability to apply knowledge in jurisprudence, ethics and professional standards for practice in Ontario; and,
- An oral examination designed to evaluate readiness for autonomous professional practice.
Once registered, a member of the College is expected to practise in accordance with applicable legislation, regulations, standards of conduct, professional guidelines, and professional codes of ethics.
Only a member of the College may offer psychological services in the province or use the title Psychologist or Psychological Associate. In addition, the use of the terms psychology or psychological, or any abbreviations or variations of these terms and titles in describing services, is restricted to members of the College. Psychologists and Psychological Associates respectively may also identify themselves with the designation C.Psych. or C.Psych.Assoc. after their names.
The College maintains a register of all current members. Information about an individual psychologist or psychological associate may be found in the searchable Public Register or obtained from the College by telephone 416-961-8817 or by e-mail: cpo@cpo.on.ca
The College has received inquiries with respect to the status of psychological associates providing services under legislative provisions such as the Statutory Accident Benefits Schedule (SABS) as well as under other public and private third party insurance programs. In 1996, the Registrar of the College sought clarification respecting providers under the SABS in an exchange of correspondence with Mr. Rob Sampson, MPP, who was at that time Parliamentary Assistant: Financial Institutions, Ministry of Finance. In his letter addressing this issue, Mr. Sampson stated:
“I have asked legal staff to review the definition in the Statutory Accident Benefits Schedule (SABS) and whether a psychological associate falls within this definition.
“I am pleased to report the definition of psychologist used in the SABS includes psychological associates. Under the SABS a “psychologist” means a person authorized by law to practise psychology. As both a psychologist and psychological associate are authorized under the Psychology Act to practice they both meet the definition under the SABS.“
More recently, the College sought clarification from the Federal Minister of Finance regarding the ability of Psychological Associates to certify eligibility for the Disability Tax Credit (DTC). In a letter from Mr. James Flaherty, Minister of Finance dated January 31, 2007 he stated:
“It is my understanding that the Ontario Psychology Act authorizes both Psychologists and Psychological Associates to practice psychology. Accordingly, holders of both titles are allowed to certify impairments with respect to an individual’s ability in mental functions necessary for everyday life for the purposes of eligibility for the DTC.”
“My officials have contacted their colleagues at the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) to communicate this understanding. The appropriate changes have been made to CRA’s administrative practices to ensure that Psychological Associates are allowed to certify impairments in mental functions necessary for everyday life.”
In summary, both Psychologists and Psychological Associates are members of the College of Psychologists. Members with either title are qualified psychological practitioners in the province of Ontario.
Questions regarding Psychologists and Psychological Associates or other matters related to the regulation and practice of psychology in Ontario may be directed to the College.
Funding for Therapy to Address Sexual Abuse by Members
Under the legislation, a person may be eligible for funding if it is alleged, in a complaint or report, that they were sexually abused by a member while a client of the member.
The legislation sets the maximum amount of funding that can be awarded as the amount that the Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP) would pay for 200 half-hour sessions of individual out-patient psychotherapy with a psychiatrist on the day the person becomes eligible. Currently, a total amount of $17,370 in funding is available. If OHIP or a private insurance plan covers some of the costs, the College would only pay the amount not covered.
Yes. The legislation specifically states the funding must be used only to pay for therapy or counselling and must be paid to the therapist or counsellor directly. The College will not pay for missed appointments. As well, funds from the program cannot be used to pay for travel, accommodation or other incidental costs even if they are incurred directly as a result of therapy.
Funding is available for up to five years from the time an application is approved by the Client Relations Committee or, if therapy to address the effects of sexual abuse began before such approval was granted, five years from day upon which the funded therapy began.
No. Any therapist or counsellor may be selected, if:
(a) it is confirmed that they have not at any time or in any jurisdiction been found guilty of professional misconduct of a sexual nature or been civilly or criminally liable for an act of a similar nature; and
(b) the therapist or counsellor is not a member of the client’s family.
No. The Committee reviews documents only.
The Client Relations Committee requires sufficient information to be satisfied that the criteria for eligibility have been met. The College recognizes however, that the information provided is very personal and sensitive. To this end, the Client Relations Committee will access only the minimum amount of information required to adequately undertake its review. An applicant’s surname will not be shared with the Committee and will be known only by College staff presenting the application to the Committee and processing the payments.
Applicants will be asked to keep confidential all information obtained through the application for funding process, including the fact that funding has been granted and the reasons, if any, given by the Committee for granting the funding. Furthermore, a decision by the Committee concerning eligibility for funding does not constitute a finding against the member and shall not be considered by any other Committee of the College dealing with the matter. Other College processes, including investigation and hearings may remain ongoing even during the funding application process and while funding is being provided.
Individuals who wish to apply for funding for therapy or counselling under this program, may contact the Deputy Registrar, Mr. Barry Gang. His contact information is available below. Mr. Gang will answer any further questions applicants may have and will provide assistance in applying for funding.
Applicants will be asked to provide a written statement from the therapist or counsellor to the Client Relations Committee indicating:
(a) confirmation that the therapy or counselling is being provided to the client and that the funds are being devoted only to the therapy or counselling;
(b) a short description of the therapy or counselling to be offered;
(c) the fees to be charged for the service;
(d) whether the therapist or counsellor has liability insurance; and
(e) the details of the therapist’s or counsellor’s training and experience and whether the therapist or counsellor is a member of a Regulated Health Profession;
If the therapist or counsellor is not a Regulated Health Professional, the applicant will be asked to sign a document indicating that they understand that the therapist or counsellor is not subject to professional discipline.